Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
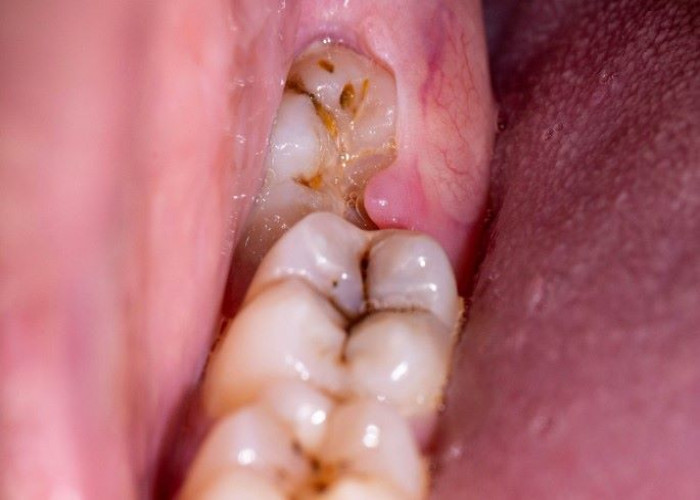
Impacted wisdom teeth

Impacted wisdom teeth are third molars at the back of the mouth that don't have enough room to emerge or develop normally. They may be partially or fully impacted, meaning they are covered by gum tissue, bone, or adjacent teeth.
Impacted wisdom teeth can cause a variety of problems, including pain, infection, gum disease, damage to surrounding teeth, and even cysts or tumors. Common symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth include pain, swelling, tenderness, bad breath, and difficulty opening the mouth.
If impacted wisdom teeth are causing symptoms or other problems, treatment may be necessary. In some cases, they may need to be removed by an oral surgeon. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, and patients may be given sedation to help them relax during the procedure. Recovery time can vary, but most people can return to normal activities within a few days to a week.
Regular dental check-ups and X-rays can help identify impacted wisdom teeth before they cause problems, and in some cases, early extraction may be recommended to prevent potential complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen jaw
- Bleeding from gums
- Swollen gums
- Jaw pain
- Bad breath (halitosis)
Disease Causes
Impacted wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth (third molars) become impacted because they don't have enough room to come in (erupt) or develop normally.
Wisdom teeth usually emerge sometime between the ages of 17 and 25. Some people have wisdom teeth that emerge without any problems and line up with the other teeth behind the second molars. In many cases, however, the mouth is too crowded for third molars to develop normally. These crowded third molars become trapped (impacted).
An impacted wisdom tooth may partially emerge so that some of the crown is visible (partially impacted), or it may never break through the gums (fully impacted). Whether partially or fully impacted, the tooth may:
- Grow at an angle toward the next tooth (second molar)
- Grow at an angle toward the back of the mouth
- Grow at a right angle to the other teeth, as if the wisdom tooth is "lying down" within the jawbone
- Grow straight up or down like other teeth but stay trapped within the jawbone
Disease Prevents
Impacted wisdom teeth
You can't keep an impaction from occurring, but keeping regular six-month dental appointments for cleaning and checkups enables your dentist to monitor the growth and emergence of your wisdom teeth. Regularly updated dental X-rays may indicate impacted wisdom teeth before any symptoms develop.
Disease Treatments
If your impacted wisdom teeth are likely to be difficult to treat or if you have medical conditions that may increase surgical risks, your dentist will likely ask you to see an oral surgeon to discuss the best course of action.
Managing asymptomatic wisdom teeth
If impacted wisdom teeth aren't causing symptoms or apparent dental problems, they're called asymptomatic. Some disagreement exists in the dental community about how to manage asymptomatic impacted wisdom teeth. Research on this topic doesn't strongly favor one strategy over the other.
Some dentists and oral surgeons recommend removing asymptomatic wisdom teeth to prevent future potential problems. They argue:
- Symptom-free wisdom teeth may not be free of disease.
- If there isn't enough space for the teeth to erupt, it's often hard to get to them and clean them properly.
- Serious complications with wisdom teeth happen less often in younger adults.
- The procedure is more difficult and more likely to cause complications later in life, particularly among older adults.
Other dentists and oral surgeons recommend a more conservative approach. They note:
- There isn't enough evidence to suggest that impacted wisdom teeth not causing problems in young adulthood will later cause problems.
- The expense and risks of the procedure don't justify the expected benefit.
With a conservative approach, your dentist will monitor your teeth for decay, gum disease or other complications. He or she may recommend removing a tooth if problems arise.
Surgical removal
Impacted wisdom teeth that are causing pain or other dental problems are usually surgically removed (extracted). Extraction of a wisdom tooth is usually required for:
- Infection or gum disease (periodontal disease) involving the wisdom teeth
- Tooth decay in partially erupted wisdom teeth
- Cysts or tumors involving the wisdom teeth
- Wisdom teeth that are causing damage to neighboring teeth
Extraction is almost always done as an outpatient procedure, so you'll go home the same day. The process includes:
- Sedation or anesthesia. You may have local anesthesia, which numbs your mouth; sedation anesthesia that depresses your consciousness; or general anesthesia, which makes you lose consciousness.
- Tooth removal. During an extraction your dentist or oral surgeon makes an incision in your gums and removes any bone that blocks access to the impacted tooth root. After removing the tooth, the dentist or oral surgeon typically closes the wound with stitches and packs the empty space (socket) with gauze.
Wisdom tooth extractions may cause some pain and bleeding, as well as swelling of the site or jaw. Temporarily, some people have trouble opening their mouth wide due to swelling of the jaw muscles. You'll receive instructions for caring for wounds and for managing pain and swelling, such as taking pain medication and using cold compresses to reduce swelling.
Much less commonly, some people may experience:
- Painful dry socket, or exposure of bone if the post-surgical blood clot is lost from the socket
- Infection in the socket from bacteria or trapped food particles
- Damage to nearby teeth, nerves, jawbone or sinuses
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Impacted wisdom teeth and Learn More about Diseases

Rett syndrome

Specific phobias
Pyoderma gangrenosum

Premature ejaculation

Bradycardia
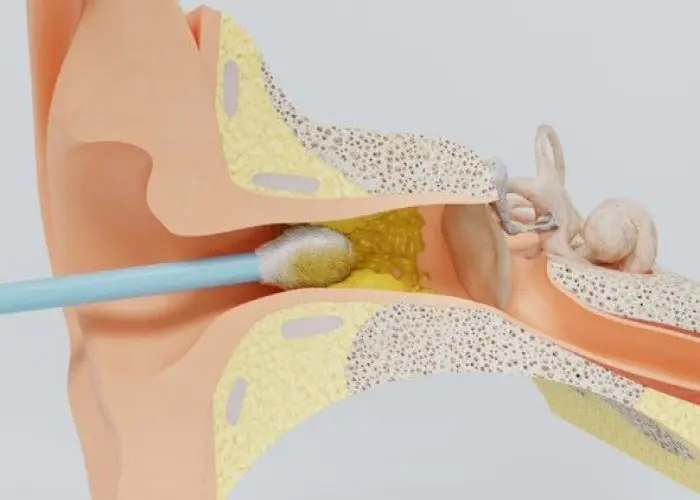
Earwax blockage

Rotavirus

Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
impacted wisdom teeth, প্রভাবিত আক্কেল দাঁত
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.