Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Heart arrhythmia

Heart arrhythmia refers to an abnormality in the rhythm or rate of the heartbeat. Normally, the heart beats in a regular rhythm, and the electrical impulses that control the heartbeat are generated by a natural pacemaker in the heart called the sinoatrial (SA) node.
However, in cases of arrhythmia, the electrical impulses may be irregular or the heart may beat too fast, too slow, or with an irregular pattern. This can result in various symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, fatigue, chest pain, and even fainting.
There are many different types of arrhythmias, which can be classified based on their origin in the heart, duration, and other factors. Some common types of arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and bradycardia.
Causes of arrhythmia may include underlying heart conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, or congenital heart defects, as well as lifestyle factors such as stress, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption. Treatment of arrhythmia may include medication, electrical cardioversion, or catheter ablation, among other options.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- Slow heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Anxiety
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Heavy sweating (diaphoresis)
- Fainting (syncope)
Disease Causes
Heart arrhythmia
To understand the cause of heart arrhythmias, it may be helpful to know how the heart typically works.
How does the heart beat?
The heart is made of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles).
The heart's rhythm is normally controlled by a natural pacemaker (the sinus node) in the right upper chamber (atrium). The sinus node sends electrical signals that normally start each heartbeat. These electrical signals move across the atria, causing the heart muscles to squeeze (contract) and pump blood into the ventricles.
Next, the signals arrive at a cluster of cells called the AV node, where they slow down. This slight delay allows the ventricles to fill with blood. When the electrical signals reach the ventricles, the chambers contract and pump blood to the lungs or to the rest of the body.
In a healthy heart, this heart signaling process usually goes smoothly, resulting in a normal resting heart rate of 60 to 100 beats a minute.
Things that can cause an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) include:
- Current heart attack or scarring from a previous heart attack
- Blocked arteries in the heart (coronary artery disease)
- Changes to the heart's structure, such as from cardiomyopathy
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Infection with COVID-19
- Overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism)
- Sleep apnea
- Underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
- Certain medications, including cold and allergy drugs bought without a prescription
- Drinking too much alcohol or caffeine
- Drug abuse
- Genetics
- Smoking
- Stress or anxiety
Disease Prevents
Heart arrhythmia
Lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of heart disease may help prevent heart arrhythmias. A heart-healthy lifestyle includes:
- Eating a heart-healthy diet
- Staying physically active
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Not smoking
- Limiting or avoiding caffeine and alcohol
- Reducing stress, as intense stress and anger can cause heart rhythm problems
- Using medications as directed and telling your doctor about all the medicines you take, including those bought without a prescription
Disease Treatments
Treatment for heart arrhythmias depends on whether you have a fast heartbeat (tachycardia) or slow heartbeat (bradycardia). Some heart arrhythmias do not need treatment. Your doctor may recommend regular checkups to monitor your condition.
Heart arrhythmia treatment is usually only needed if the irregular heartbeat is causing significant symptoms, or if the condition is putting you at risk of more-serious heart problems. Treatment for heart arrhythmias may include medications, therapies such as vagal maneuvers, cardioversion, catheter procedures or heart surgery.
Medications
Medications used to treat heart arrhythmias depend on the type of arrhythmia and potential complications.
For example, drugs to control the heart rate and restore a normal heart rhythm are often prescribed for most people with tachycardia.
If you have atrial fibrillation, blood thinners may be prescribed to prevent blood clots. It's very important to take the medications exactly as directed by your doctor in order to reduce the risk of complications.
Therapies
Therapies to treat heart arrhythmias include vagal maneuvers and cardioversion to stop the irregular heartbeat.
- Vagal maneuvers. If you have a very fast heartbeat due to supraventricular tachycardia, your doctor may recommend this therapy. Vagal maneuvers affect the nervous system that controls your heartbeat (vagus nerves), often causing your heart rate to slow. For example, you may be able to stop an arrhythmia by holding your breath and straining, dunking your face in ice water, or coughing. Vagal maneuvers don't work for all types of arrhythmias.
- Cardioversion. This method to reset the heart rhythm may be done with medications or as a procedure. Your doctor may recommend this treatment if you have a certain type of arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation.
- During the cardioversion procedure, a shock is delivered to your heart through paddles or patches on your chest. The current affects the electrical impulses in your heart and can restore a normal rhythm.
Surgery or other procedures
Treatment for heart arrhythmias may also involve catheter procedures or surgery to implant a heart (cardiac) device. Certain arrhythmias may require open-heart surgery.
Types of procedures and surgeries used to treat heart arrhythmias include:
- Catheter ablation. In this procedure, the doctor threads one or more catheters through the blood vessels to the heart. Electrodes at the catheter tips use heat or cold energy to create tiny scars in your heart to block abnormal electrical signals and restore a normal heartbeat.
- Pacemaker. If slow heartbeats (bradycardias) don't have a cause that can be corrected, doctors often treat them with a pacemaker because there aren't any medications that can reliably speed up the heart.
- A pacemaker is a small device that's usually implanted near the collarbone. One or more electrode-tipped wires run from the pacemaker through the blood vessels to the inner heart. If the heart rate is too slow or if it stops, the pacemaker sends out electrical impulses that stimulate the heart to beat at a steady rate.
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). Your doctor may recommend this device if you're at high risk of developing a dangerously fast or irregular heartbeat in the lower heart chambers (ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation). If you have had sudden cardiac arrest or have certain heart conditions that increase your risk of sudden cardiac arrest, your doctor may also recommend an ICD.
- An ICD is a battery-powered unit that's implanted under the skin near the collarbone — similar to a pacemaker. One or more electrode-tipped wires from the ICD run through veins to the heart. The ICD continuously monitors your heart rhythm.
- If the ICD detects an abnormal heart rhythm, it sends out low- or high-energy shocks to reset the heart to a normal rhythm. An ICD doesn't prevent an irregular heart rhythm from occurring, but it treats it if it occurs.
- Maze procedure. In the maze procedure, a surgeon makes a series of incisions in the heart tissue in the upper half of your heart (atria) to create a pattern (or maze) of scar tissue. Because scar tissue doesn't conduct electricity, it interferes with stray electrical impulses that cause some types of arrhythmia.
- The maze procedure is usually reserved for people who don't get better with other treatments or who are having open-heart surgery for other reasons.
- Coronary bypass surgery. If you have severe coronary artery disease in addition to a heart arrhythmia, your doctor may perform coronary bypass surgery. This procedure may improve the blood flow to your heart.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Heart arrhythmia and Learn More about Diseases
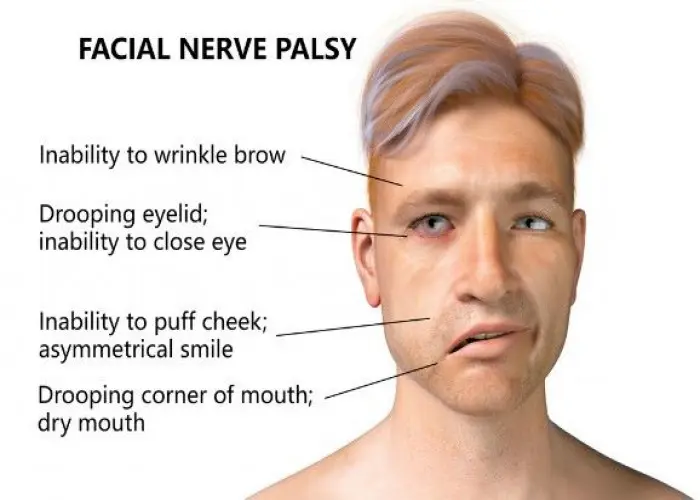
Facial palsy

Heart arrhythmia
Myocarditis
Brain tumor

Pubic lice (crabs)

Dysentery

Bartholin's cyst

Patellofemoral pain syndrome
heart arrhythmia, হার্ট অ্যারিথমিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.