Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
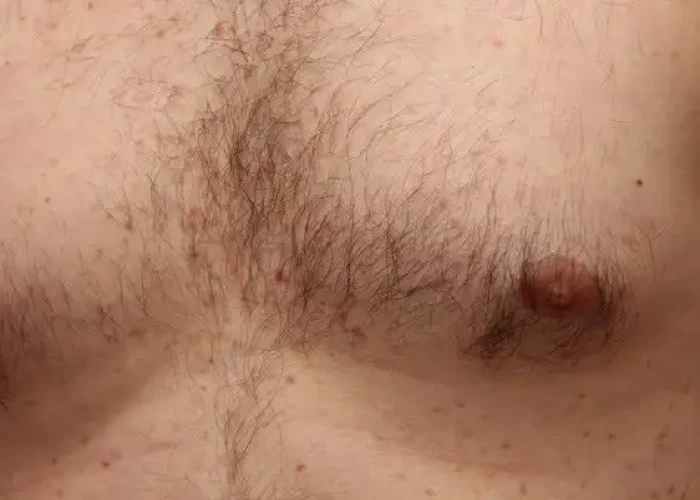
Folliculitis
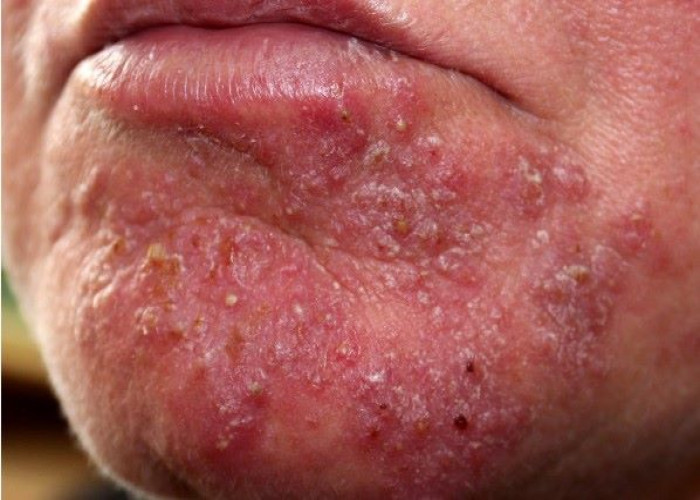
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed or infected. It can affect any part of the body where hair grows, but it most commonly occurs on the scalp, face, neck, chest, back, and buttocks.
Folliculitis can be caused by a number of factors, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and irritation from shaving or other hair removal methods. It can also occur as a result of skin conditions such as acne or dermatitis.
Symptoms of folliculitis include small, red bumps or pustules around the hair follicles, which may be itchy, tender, or painful. In severe cases, there may be crusting, scaling, or scarring of the affected area.
Treatment for folliculitis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Mild cases can often be managed with self-care measures such as warm compresses, gentle cleansing, and avoiding irritants or tight clothing. Topical medications such as antibiotics or antifungal creams may also be prescribed to reduce inflammation and fight infection.
In more severe cases or if the infection spreads, oral antibiotics or antifungal medications may be necessary. In some cases, corticosteroid creams or oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching.
Prevention of folliculitis involves maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding sharing personal items like towels or razors, and using appropriate hair removal methods. For those who are prone to developing folliculitis, a dermatologist may recommend an ongoing skin care regimen to help manage the condition.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Skin bumps
- Acne (Pimple)
- Itching
- Swollen lump or skin nodules
- Pus-filled blisters that break open and crust over
Disease Causes
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is most often caused by an infection of hair follicles with Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria. Folliculitis may also be caused by viruses, fungi and even an inflammation from ingrown hairs.
Follicles are densest on your scalp, and they occur everywhere on your body except your palms, soles, lips and mucous membranes.
Disease Prevents
Folliculitis
You can try to prevent folliculitis from coming back with these tips:
- Avoid tight clothes. It helps to reduce friction between your skin and clothing.
- Dry out your rubber gloves between uses. If you wear rubber gloves regularly, after each use turn them inside out, rinse with soap and water, and dry thoroughly.
- Avoid shaving, if possible. For men with razor bumps (pseudofolliculitis), growing a beard may be a good option if you don't need a clean-shaven face.
- Shave with care. If you shave, adopt habits such as the following to help control symptoms by reducing the closeness of the shave and the risk of damaging your skin:
- Shaving less frequently
- Washing your skin with warm water and antibacterial soap before shaving
- Using a washcloth or cleansing pad in a gentle circular motion to raise embedded hairs before shaving
- Applying a good amount of shaving lotion before shaving
- Shaving in the direction of hair growth, though one study found that men who shaved against the grain had fewer skin bumps. See what works best for you.
- Avoiding shaving too close by using an electric razor or guarded blade and by not stretching the skin
- Using a sharp blade and rinsing it with warm water after each stroke
- Applying moisturizing lotion after you shave
- Avoiding the sharing of razors, towels and washcloths
- Considering hair-removing products (depilatories) or other methods of hair removal. Though they, too, may irritate the skin.
- Use only clean hot tubs and heated pools. And if you own a hot tub or a heated pool, clean it regularly and add chlorine as recommended.
- Talk with your doctor. Depending on your situation and frequency of recurrences, your doctor may suggest controlling bacterial growth in your nose with a five-day regimen of antibacterial ointment and using a body wash with chlorhexidine (Hibiclens, Hibistat). Further study is needed to prove the effectiveness of these steps.
Disease Treatments
Treatments for folliculitis depend on the type and severity of your condition, what self-care measures you've already tried and your preferences. Options include medications and interventions such as laser hair removal. Even if treatment helps, the infection may come back.
Medications
- Creams or pills to control infection. For mild infections, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic cream, lotion or gel. Oral antibiotics aren't routinely used for folliculitis. But for a severe or recurrent infection, your doctor may prescribe them.
- Creams, shampoos or pills to fight fungal infections. Antifungals are for infections caused by yeast rather than bacteria. Antibiotics aren't helpful in treating this type.
- Creams or pills to reduce inflammation. If you have mild eosinophilic folliculitis, your doctor may suggest you try a steroid cream to ease the itching. If you have HIV/AIDS, you may see improvement in your eosinophilic folliculitis symptoms after antiretroviral therapy.
Other interventions
- Minor surgery. If you have a large boil or carbuncle, your doctor may make a small incision in it to drain the pus. This may relieve pain, speed recovery and lessen scarring. Your doctor may then cover the area with sterile gauze in case pus continues to drain.
- Laser hair removal. If other treatments fail, long-term hair removal with laser therapy may clear up the infection. This method is expensive and often requires several treatments. It permanently removes hair follicles, thus reducing the density of the hair in the treated area. Other possible side effects include discolored skin, scarring and blistering.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Folliculitis and Learn More about Diseases

Low blood pressure (hypotension)
Seborrheic dermatitis
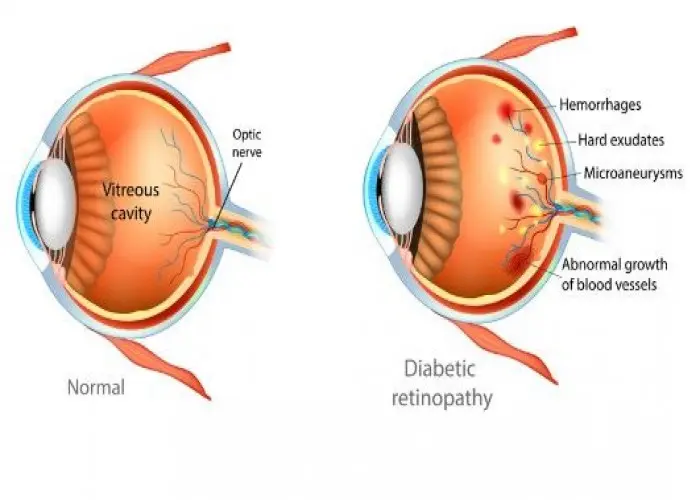
Diabetic retinopathy
Systemic mastocytosis
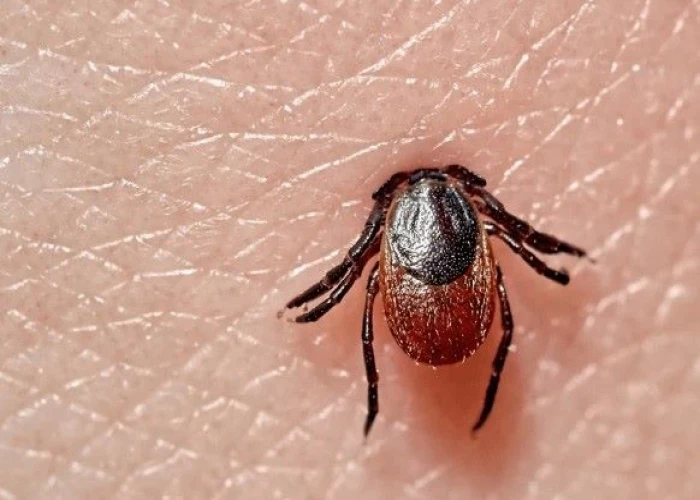

Lyme disease

Male hypogonadism

Eating disorders
Hemifacial spasm
folliculitis, ফলিকুলাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.