Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Diverticulitis
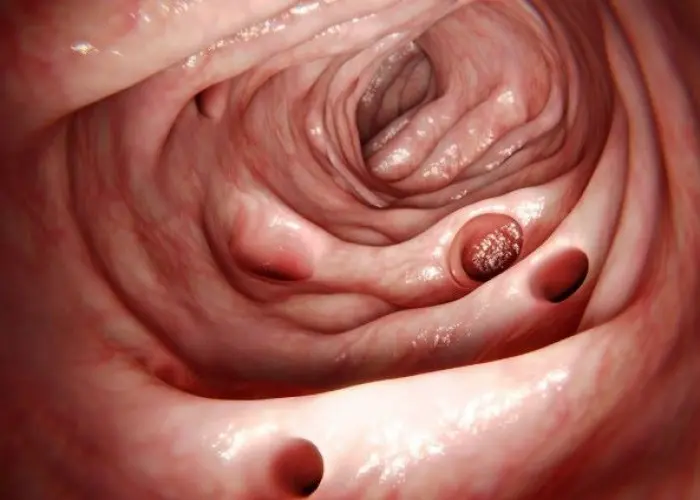
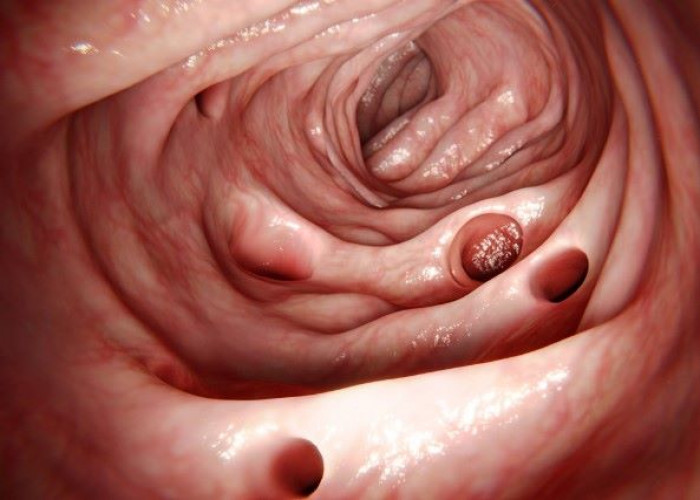
Diverticulitis is a medical condition that occurs when small pouches, called diverticula, that form in the walls of the colon become inflamed or infected. The condition is more common in older adults and may occur as a result of a low-fiber diet, constipation, obesity, or lack of exercise.
Symptoms of diverticulitis can include abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. In some cases, the condition can lead to complications such as abscesses, perforations, or blockages in the colon.
Diagnosis of diverticulitis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging tests such as a CT scan or ultrasound to look for signs of inflammation or infection in the colon.
Treatment of diverticulitis may involve antibiotics to treat the infection, as well as pain medications and a liquid or low-fiber diet to allow the colon to rest and heal. In severe cases or in the presence of complications, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected part of the colon.
Prevention of diverticulitis involves maintaining a healthy diet high in fiber, drinking plenty of water, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. If you have a history of diverticulitis, it is important to avoid certain foods that may trigger symptoms, such as nuts, seeds, and popcorn.
In conclusion, diverticulitis is a condition that occurs when small pouches in the colon become inflamed or infected, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, and diarrhea. Treatment may involve antibiotics, pain management, and a low-fiber diet, while prevention involves maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle. If you suspect that you may have diverticulitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Abdomen pain
- Lower abdomen pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever
- Abdominal tenderness
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
Disease Causes
Diverticulitis
Diverticula usually develop when naturally weak places in your colon give way under pressure. This causes marble-sized pouches to protrude through the colon wall.
Diverticulitis occurs when diverticula tear, resulting in inflammation, and in some cases, infection.
Disease Prevents
Diverticulitis
To help prevent diverticulitis:
- Exercise regularly. Exercise promotes normal bowel function and reduces pressure inside your colon. Try to exercise at least 30 minutes on most days.
- Eat more fiber. A high-fiber diet decreases the risk of diverticulitis. Fiber-rich foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains, soften waste material and help it pass more quickly through your colon. Eating seeds and nuts isn't associated with developing diverticulitis.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Fiber works by absorbing water and increasing the soft, bulky waste in your colon. But if you don't drink enough liquid to replace what's absorbed, fiber can be constipating.
- Avoid smoking. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of diverticulitis.
Disease Treatments
Treatment depends on the severity of your signs and symptoms.
Uncomplicated diverticulitis
If your symptoms are mild, you may be treated at home. Your doctor is likely to recommend:
- Antibiotics to treat infection, although new guidelines state that in very mild cases, they may not be needed.
- A liquid diet for a few days while your bowel heals. Once your symptoms improve, you can gradually add solid food to your diet.
This treatment is successful in most people with uncomplicated diverticulitis.
Complicated diverticulitis
If you have a severe attack or have other health problems, you'll likely need to be hospitalized. Treatment generally involves:
- Intravenous antibiotics
- Insertion of a tube to drain an abdominal abscess, if one has formed
Surgery
You'll likely need surgery to treat diverticulitis if:
- You have a complication, such as a bowel abscess, fistula or obstruction, or a puncture (perforation) in the bowel wall
- You have had multiple episodes of uncomplicated diverticulitis
- You have a weakened immune system
There are two main types of surgery:
- Primary bowel resection. The surgeon removes diseased segments of your intestine and then reconnects the healthy segments (anastomosis). This allows you to have normal bowel movements. Depending on the amount of inflammation, you may have open surgery or a minimally invasive (laparoscopic) procedure.
- Bowel resection with colostomy. If you have so much inflammation that it's not possible to rejoin your colon and rectum, the surgeon will perform a colostomy. An opening (stoma) in your abdominal wall is connected to the healthy part of your colon. Waste passes through the opening into a bag. Once the inflammation has eased, the colostomy may be reversed and the bowel reconnected.
Follow-up care
Your doctor may recommend colonoscopy six weeks after you recover from diverticulitis, especially if you haven't had the test in the previous year. There doesn't appear to be a direct link between diverticular disease and colon or rectal cancer. But colonoscopy — which is risky during a diverticulitis attack — can exclude colon cancer as a cause of your symptoms.
After successful treatment, your doctor may recommend surgery to prevent future episodes of diverticulitis. The decision on surgery is an individual one and is often based on the frequency of attacks and whether complications have occurred.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Diverticulitis and Learn More about Diseases
Guillain-Barre syndrome

Trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder)

Herniated disk

Pulmonary fibrosis

Phantom pain
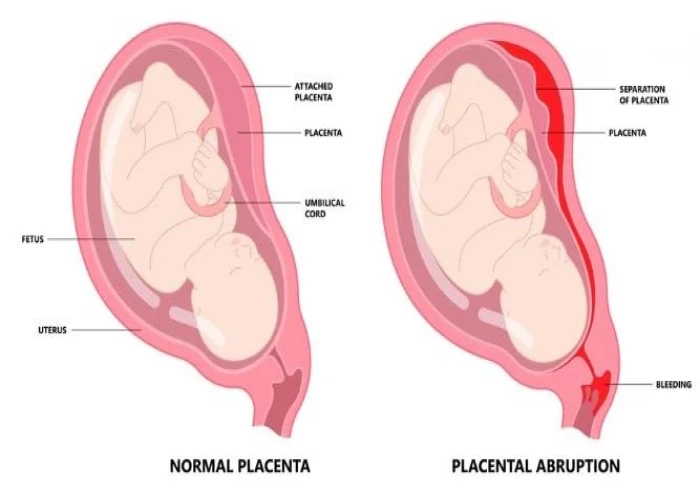
Placenta accreta

Lip cancer

Peripheral nerve injuries
diverticulitis, ডাইভার্টিকুলাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.