Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
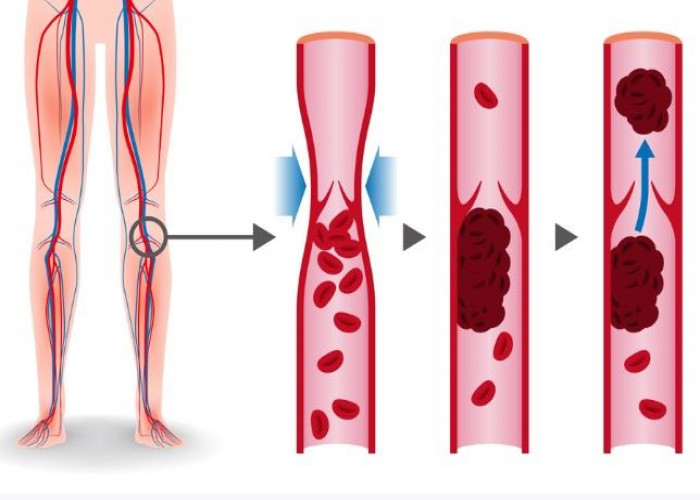
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)

Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body, usually in your legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling but also can occur with no symptoms.
You can get DVT if you have certain medical conditions that affect how your blood clots. A blood clot in your legs can also happen if you don't move for a long time, such as after you have surgery or an accident, when you're traveling a long distance, or when you're on bed rest.
Deep vein thrombosis can be very serious because blood clots in your veins can break loose, travel through your bloodstream and get stuck in your lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism). However, pulmonary embolism can occur with no evidence of DVT.
When DVT and pulmonary embolism occur together, it's called venous thromboembolism (VTE).
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen leg
- Leg pain
- A feeling of warmth in the affected leg.
Disease Causes
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Anything that prevents your blood from flowing or clotting normally can cause a blood clot.
The main causes of DVT are damage to a vein from surgery or trauma and inflammation due to infection or injury.
Disease Prevents
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis include the following:
- Avoid sitting still. If you have had surgery or have been on bed rest for other reasons, try to get moving as soon as possible. If you're sitting for a while, don't cross your legs, which can block blood flow. If you're traveling a long distance by car, stop every hour or so and walk around.
- If you're on a plane, stand or walk occasionally. If you can't do that, exercise your lower legs. Try raising and lowering your heels while keeping your toes on the floor, then raising your toes with your heels on the floor.
- Don't smoke. Smoking increases your risk of getting DVT.
- Exercise and manage your weight. Obesity is a risk factor for DVT. Regular exercise lowers your risk of blood clots, which is especially important for people who sit a lot or travel frequently.
Disease Treatments
There are three main goals to DVT treatment.
- Prevent the clot from getting bigger.
- Prevent the clot from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs.
- Reduce your chances of another DVT.
DVT treatment options include:
- Blood thinners. DVT is most commonly treated with anticoagulants, also called blood thinners. These drugs don't break up existing blood clots, but they can prevent clots from getting bigger and reduce your risk of developing more clots.
- Blood thinners may be taken by mouth or given by IV or an injection under the skin. Heparin is typically given by IV. The most commonly used injectable blood thinners for DVT are enoxaparin (Lovenox) and fondaparinux (Arixtra).
- After taking an injectable blood thinner for a few days, your doctor may switch you to a pill. Examples of blood thinners that you swallow include warfarin (Jantoven) and dabigatran (Pradaxa).
- Certain blood thinners do not need to be given first with IV or injection. These drugs are rivaroxaban (Xarelto), apixaban (Eliquis) or edoxaban (Savaysa). They can be started immediately after diagnosis.
- You might need to take blood thinner pills for three months or longer. It's important to take them exactly as prescribed to prevent serious side effects.
- If you take warfarin, you'll need regular blood tests to check how long it takes your blood to clot. Pregnant women shouldn't take certain blood-thinning medications.
- Clot busters. Also called thrombolytics, these drugs might be prescribed if you have a more serious type of DVT or PE, or if other medications aren't working.
- These drugs are given either by IV or through a tube (catheter) placed directly into the clot. Clot busters can cause serious bleeding, so they're usually only used for people with severe blood clots.
- Filters. If you can't take medicines to thin your blood, you might have a filter inserted into a large vein — the vena cava — in your abdomen. A vena cava filter prevents clots that break loose from lodging in your lungs.
- Compression stockings. These special knee socks reduce the chances that your blood will pool and clot. To help prevent swelling associated with deep vein thrombosis, wear them on your legs from your feet to about the level of your knees. You should wear these stockings during the day for at least two years, if possible.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and Learn More about Diseases
Hidradenitis suppurativa

Factor V Leiden

IgA nephropathy (Berger's disease)
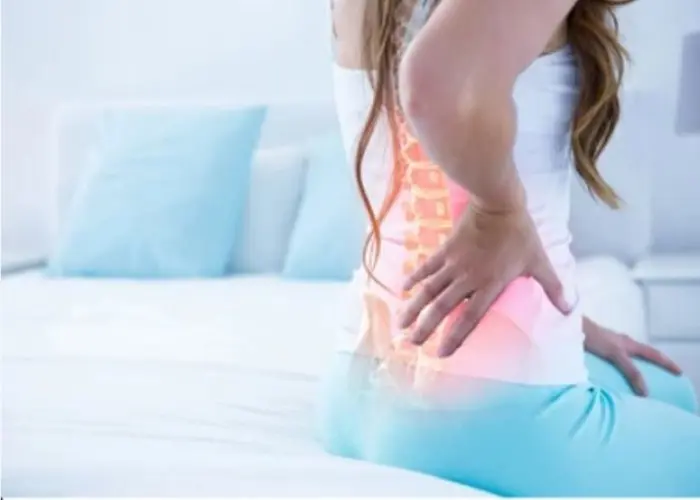

Back pain
Drug allergy

Syringomyelia

Galactorrhea
Paraneoplastic syndromes of the nervous system
deep vein thrombosis, DVT, Venous thrombosis, গভীর শিরা থ্রোম্বোসিস, ডিভিটি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.