Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Contact dermatitis
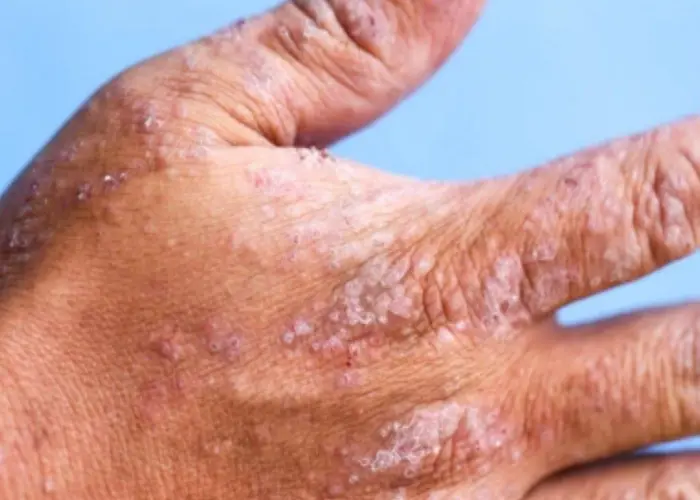
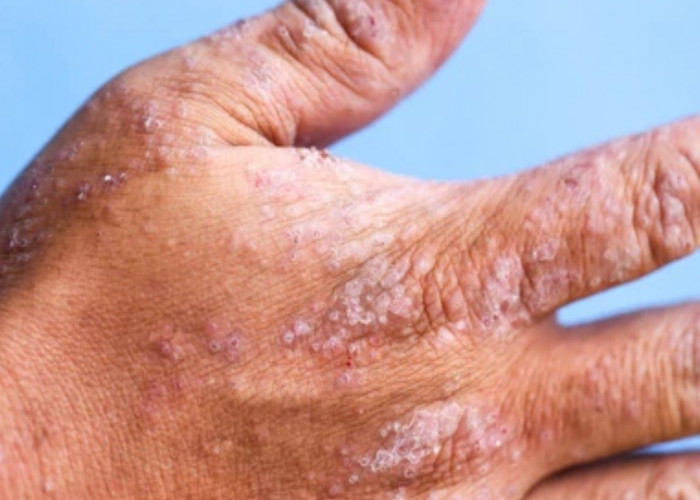
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. The condition can cause a rash or red, itchy, and swollen skin. The severity of the reaction depends on the type and amount of the irritant or allergen, as well as the individual's sensitivity to it.
Contact dermatitis can be caused by a variety of substances, including:
- Soaps and detergents
- Cosmetics and fragrances
- Metals such as nickel and gold
- Latex
- Plants such as poison ivy and poison oak
- Chemicals used in hair dyes, nail polish, and other beauty products
- Certain medications
The symptoms of contact dermatitis usually appear within a few hours to a few days after exposure to the irritant or allergen. They may include:
- Redness and swelling of the skin
- Blisters or hives
- Itching or burning
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
- Pain or tenderness
Treatment for contact dermatitis usually involves avoiding the substance that caused the reaction and taking steps to relieve the symptoms. Over-the-counter topical creams or ointments such as hydrocortisone may help relieve itching and inflammation. In more severe cases, prescription medications such as corticosteroids or oral antihistamines may be necessary.
Prevention is key when it comes to contact dermatitis. Avoiding known irritants or allergens and wearing protective clothing, gloves, and other gear can help reduce the risk of exposure. In addition, keeping the skin moisturized can help prevent dry, cracked skin that is more susceptible to contact dermatitis.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Skin rash
- Itching
- Dry skin
- Red skin
- Cracked skin
- Skin bumps
- Watery blisters
- Skin pain or burning sensation
Disease Causes
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is caused by a substance you're exposed to that irritates your skin or triggers an allergic reaction. The substance could be one of thousands of known allergens and irritants. Some of these substances may cause both irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type. This nonallergic skin reaction occurs when a substance damages your skin's outer protective layer.
Some people react to strong irritants after a single exposure. Others may develop signs and symptoms after repeated exposures to even mild irritants. And some people develop a tolerance to the substance over time.
Common irritants include:
- Solvents
- Rubbing alcohol
- Bleach and detergents
- Shampoos, permanent wave solutions
- Airborne substances, such as sawdust or wool dust
- Plants
- Fertilizers and pesticides
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when a substance to which you're sensitive (allergen) triggers an immune reaction in your skin. It usually affects only the area that came into contact with the allergen. But it may be triggered by something that enters your body through foods, flavorings, medicine, or medical or dental procedures (systemic contact dermatitis).
You may become sensitized to a strong allergen such as poison ivy after a single exposure. Weaker allergens may require multiple exposures over several years to trigger an allergy. Once you develop an allergy to a substance, even a small amount of it can cause a reaction.
Common allergens include:
- Nickel, which is used in jewelry, buckles and many other items
- Medications, such as antibiotic creams and oral antihistamines
- Balsam of Peru, which is used in many products, such as perfumes, cosmetics, mouth rinses and flavorings
- Formaldehyde, which is in preservatives, disinfectants and clothing
- Personal care products, such as deodorants, body washes, hair dyes, cosmetics and nail polish
- Plants such as poison ivy and mango, which contain a highly allergenic substance called urushiol
- Airborne substances, such as ragweed pollen and spray insecticides
- Products that cause a reaction when you're in the sun (photoallergic contact dermatitis), such as some sunscreens and oral medications
Children develop the condition from the usual offenders and also from exposure to diapers, baby wipes, sunscreens, clothing with snaps or dyes, and so on.
Disease Prevents
Contact dermatitis
General prevention steps include the following:
- Avoid irritants and allergens. Try to identify and avoid substances that irritate your skin or cause an allergic reaction.
- Wash your skin. You might be able to remove most of the rash-causing substance if you wash your skin right away after coming into contact with it. Use a mild, fragrance-free soap and warm water. Rinse completely. Also wash any clothing or other items that may have come into contact with a plant allergen, such as poison ivy.
- Wear protective clothing or gloves. Face masks, goggles, gloves and other protective items can shield you from irritating substances, including household cleansers.
- Apply an iron-on patch to cover metal fasteners next to your skin. This can help you avoid a reaction to jean snaps, for example.
- Apply a barrier cream or gel. These products can provide a protective layer for your skin. For example, an over-the-counter skin cream containing bentoquatam (IvyBlock) may prevent or lessen your skin's reaction to poison ivy.
- Use moisturizer. Regularly applying moisturizing lotions can help restore your skin's outermost layer and keep your skin supple.
- Take care around pets. Allergens from plants, such as poison ivy, can cling to pets and then be spread to people.
Disease Treatments
If home care steps don't ease your signs and symptoms, your doctor may prescribe medications. Examples include:
- Steroid creams or ointments. These topically applied creams or ointments help soothe the rash of contact dermatitis. A topical steroid may be applied one or two times a day for two to four weeks.
- Oral medications. In severe cases, your doctor may prescribe oral corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, antihistamines to relieve itching or antibiotics to fight a bacterial infection.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Contact dermatitis and Learn More about Diseases
Bone cancer
Mouth Ulcer

Plantar warts

Desmoplastic small round cell tumors

Low sex drive in women
Facial palsy

Sleepwalking
Pityriasis rosea
Contact dermatitis, Contact dermatitis treatment, কন্ট্রাক্ট ডার্মাটাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.