 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Cholecystitis
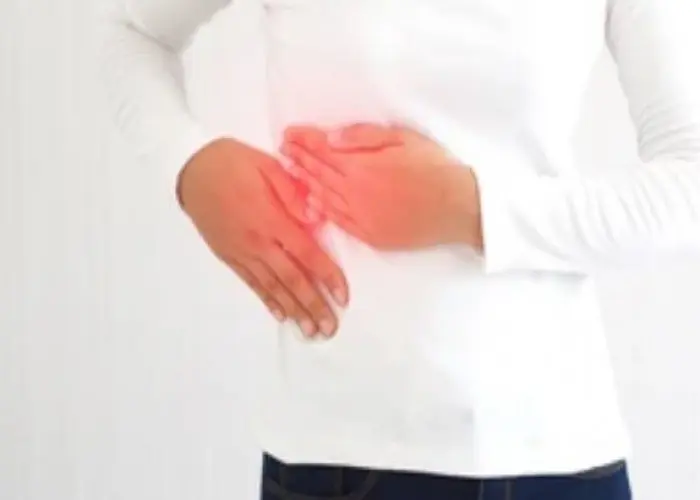
Cholecystitis is a condition in which the gallbladder becomes inflamed, typically due to the presence of gallstones or a blockage in the ducts that transport bile. The most common symptom of cholecystitis is pain in the upper right abdomen, which can be severe and may radiate to the back or shoulder. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, fever, and jaundice. Treatment options for cholecystitis may include antibiotics to treat any underlying infection, pain management, and surgery to remove the gallbladder, known as cholecystectomy. With prompt and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for cholecystitis is generally good.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Upper right or center abdomen pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever
- Pain that spreads to your right shoulder or back
Disease Causes
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis occurs when your gallbladder becomes inflamed. Gallbladder inflammation can be caused by:
- Gallstones. Most often, cholecystitis is the result of hard particles that develop in your gallbladder (gallstones). Gallstones can block the tube (cystic duct) through which bile flows when it leaves the gallbladder. Bile builds up, causing inflammation.
- Tumor. A tumor may prevent bile from draining out of your gallbladder properly, causing bile buildup that can lead to cholecystitis.
- Bile duct blockage. Kinking or scarring of the bile ducts can cause blockages that lead to cholecystitis.
- Infection. AIDS and certain viral infections can trigger gallbladder inflammation.
- Blood vessel problems. A very severe illness can damage blood vessels and decrease blood flow to the gallbladder, leading to cholecystitis.
Disease Prevents
Cholecystitis
You can reduce your risk of cholecystitis by taking the following steps to prevent gallstones:
- Lose weight slowly. Rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones. If you need to lose weight, aim to lose 1 or 2 pounds (0.5 to about 1 kilogram) a week.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight makes you more likely to develop gallstones. To achieve a healthy weight, reduce calories and increase your physical activity. Maintain a healthy weight by continuing to eat well and exercise.
- Choose a healthy diet. Diets high in fat and low in fiber may increase the risk of gallstones. To lower your risk, choose a diet high in fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
Disease Treatments
Treatment for cholecystitis usually involves a hospital stay to control the inflammation in your gallbladder. Sometimes, surgery is needed.
At the hospital, your doctor will work to control your signs and symptoms. Treatments may include:
- Fasting. You may not be allowed to eat or drink at first in order to take stress off your inflamed gallbladder.
- Fluids through a vein in your arm. This treatment helps prevent dehydration.
- Antibiotics to fight infection. If your gallbladder is infected, your doctor likely will recommend antibiotics.
- Pain medications. These can help control pain until the inflammation in your gallbladder is relieved.
- Procedure to remove stones. Your doctor may perform a procedure called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to remove any stones blocking the bile ducts or cystic duct.
Your symptoms are likely to decrease in two or three days. However, gallbladder inflammation often returns. Most people with the condition eventually need surgery to remove the gallbladder.
Gallbladder removal surgery is called a cholecystectomy. Usually, this is a minimally invasive procedure, involving a few tiny incisions in your abdomen (laparoscopic cholecystectomy). An open procedure, in which a long incision is made in your abdomen, is rarely required.
The timing of surgery depends on the severity of your symptoms and your overall risk of problems during and after surgery. If you're at low surgical risk, surgery may be performed within 48 hours or during your hospital stay.
Once your gallbladder is removed, bile flows directly from your liver into your small intestine, rather than being stored in your gallbladder. You don't need your gallbladder to live normally.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Pethidine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing pethidine hydrochloride to relieve acute pain.
1 intramuscular injection. It is better not to over inject. Because this patient may develop addiction.
-
Hyoscine Butylbromide
1 injection intramuscularly or intravenously every 6/8 hours.
-
Hyoscine Hydrobromide
1/2 pill 3 times a day.
-
Diclofenac Sodium
1 injection into the flesh. 2/3 days can be given after 24 hours if required.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
1 pill after lunch, 1 pill after meal at night.
-
Dextrose
40/50 drops per minute. 1 Auradexon decasone is less likely to cause a reaction.
-
Promethazine Theoclate
In severe cases, first 2 tablets then 1 tablet 2 times a day.
-
Metoclopramide Hydrochloride
0.5 mg per kg of body weight should be given to meat.
-
Amoxicillin Trihydrate
Can be injected into the meat every 8 hours.
-
Ampicillin Sodium
When the patient gradually recovers, amoxicillin is stopped and ampicillin capsules are taken.
1 capsule every 6 hours for 7-10 days.
-
Cephalexin
Medicines containing cefurexin without injection containing amoxicillin.
1+1+1+1 250mg or 500mg 1+1+1.
-
Erythromycin (Oral)
For those who cannot tolerate penicillin.
1 pill of 250 mg or 500 mg or 1/2 spoon of syrup 6/8 hours after every 5/7 days.
-
Magnesium Hydroxide
Consume 2/4 teaspoon with warm water every night.
If all these medicines do not work well, douse with soft soapy water.
-
Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride
1 pill daily.
-
Metronidazole
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Vitamin B complex
B-complex medicines for patient weakness.
2cc should be injected into the flesh every morning.
Syrup: 2 spoons 3 times a day after meals.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Cholecystitis and Learn More about Diseases
Entropion

Primary biliary cholangitis
Chronic kidney disease

Irritable bowel syndrome

Celiac disease
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)

Syringomyelia
Orchitis
Cholecystitis, Acute cholecystitis, Chronic cholecystitis, কোলেসিস্টাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
