 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Adrenal cancer
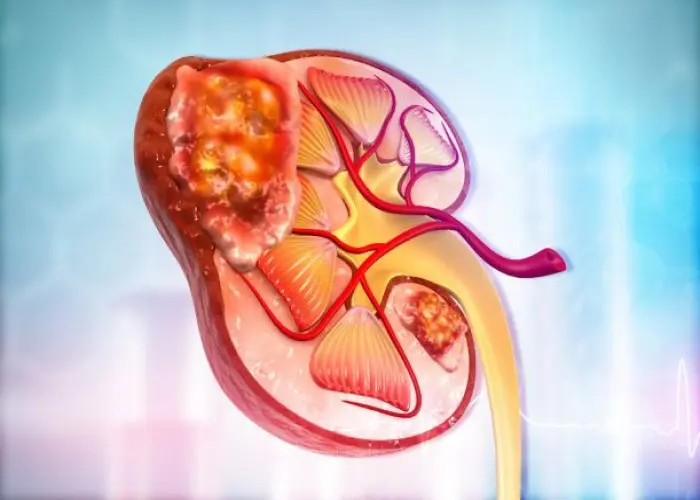
Adrenal cancer is a rare type of cancer that occurs in the adrenal glands, which are small glands located above each kidney. These glands produce hormones that regulate many important bodily functions, including blood pressure, heart rate, and the body's response to stress.
There are two main types of adrenal cancer: adrenocortical carcinoma and pheochromocytoma. Adrenocortical carcinoma is a cancer of the outer layer of the adrenal gland and affects the production of hormones, while pheochromocytoma is a tumor of the inner layer of the gland and affects the production of certain chemicals that control blood pressure.
Symptoms of adrenal cancer can vary depending on the type and stage of cancer, but may include:
- Unexpected weight loss or gain
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Back pain
- Fatigue
- Darkening of the skin
- High blood pressure
- Excessive sweating
- Headaches
- Changes in mood or behavior
Diagnosis of adrenal cancer typically involves a combination of medical imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRI, and biopsy. Treatment for adrenal cancer depends on the type, stage, and location of cancer, and may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
If you are experiencing symptoms that may be related to adrenal cancer, it's important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve your chances of full recovery and prevent potential complications.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Rapid weight gain
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Back pain
- Abdominal bloating or increased waist size
- Hair loss
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pink or purple stretch marks on the skin
- Muscle weakness
- Adrenal cancer
Disease Causes
Adrenal cancer
It's not clear what causes adrenal cancer.
Adrenal cancer forms when something creates changes (mutations) in the DNA of an adrenal gland cell. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The mutations can tell the cell to multiply uncontrollably and to continue living when healthy cells would die. When this happens, the abnormal cells accumulate and form a tumor. The tumor cells can break away and spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Adrenal cancer treatment usually involves surgery to remove all of the cancer. Other treatments might be used to prevent the cancer from coming back or if surgery isn't an option.
Surgery
The goal of surgery is to remove the entire adrenal cancer. To achieve this, doctors must remove the all of the affected adrenal gland (adrenalectomy).
If surgeons find evidence that cancer has spread to nearby structures, such as the liver or kidney, parts or all of those organs might also be removed during the operation.
Medication to reduce the risk of recurrence
An older drug that has been used to treat advanced adrenal cancer has shown promise in delaying the recurrence of the disease after surgery. Mitotane (Lysodren) may be recommended after surgery for people with a high risk of cancer recurrence. Research into mitotane for this use is ongoing.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered beams of energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy is sometimes used after adrenal cancer surgery to kill any cells that might remain. It can also help reduce pain and other symptoms of cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bone.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. For adrenal cancers that can't be removed with surgery or that return after initial treatments, chemotherapy may be an option to slow the progression of the cancer.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Adrenal cancer and Learn More about Diseases
Familial adenomatous polyposis

Restless legs syndrome

Thunderclap headaches

Alcohol use disorder
Benign peripheral nerve tumor

Head and neck cancers
Septic arthritis

Trigger finger
Adrenal cancer, Adrenal gland tumor, Adrenocortical carcinoma, অ্যাড্রিনাল ক্যান্সার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

