Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
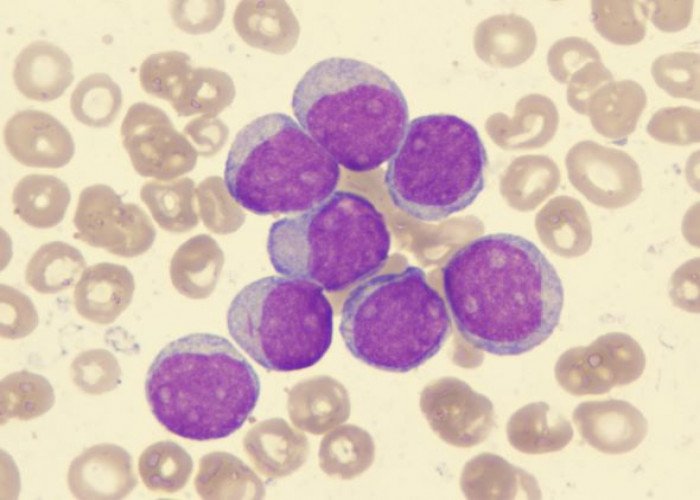
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow and blood. It is a rapidly progressing disease that affects the myeloid cells, which are immature blood cells that normally mature into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
AML is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal myeloid cells, which leads to a shortage of normal blood cells and an increased risk of infections and bleeding. Symptoms of AML may include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, frequent infections, easy bruising or bleeding, and a fever.
Diagnosis of AML typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Treatment for AML usually involves a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or stem cell transplantation. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the patient's age, overall health, and the specific subtype of AML.
With appropriate treatment, many people with AML can achieve remission and lead a normal life. However, the disease can be difficult to cure, and the outcome depends on several factors, including the patient's age, overall health, and the type and severity of the disease.
It's important for people with AML to work closely with their healthcare team to determine the best course of action and to manage their symptoms and side effects of treatment.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fever
- Bone pain
- Excessive lethargy
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Pale skin color (pallor)
- Frequent infections, such as gums or skin infections and vaginal infections
- Easy bruising or unexplained bruises
- Unusual bleeding, such as a nosebleed or bleeding gums
Disease Causes
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Acute myelogenous leukemia occurs when a bone marrow cell develops changes (mutations) in its genetic material or DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Normally, the DNA tells the cell to grow at a set rate and to die at a set time. In acute myelogenous leukemia, the mutations tell the bone marrow cell to continue growing and dividing.
When this happens, blood cell production becomes out of control. The bone marrow produces immature cells that develop into leukemic white blood cells called myeloblasts. These abnormal cells are unable to function properly, and they can build up and crowd out healthy cells.
It's not clear what causes the DNA mutations that lead to leukemia, but doctors have identified factors that increase the risk.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
Treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia depends on several factors, including the subtype of the disease, your age, your overall health and your preferences.
In general, treatment falls into two phases:
- Remission induction therapy. The purpose of the first phase of treatment is to kill the leukemia cells in your blood and bone marrow. However, remission induction usually doesn't wipe out all of the leukemia cells, so you need further treatment to prevent the disease from returning.
- Consolidation therapy. Also called post-remission therapy or maintenance therapy, this phase of treatment is aimed at destroying the remaining leukemia cells. It's considered crucial to decreasing the risk of relapse.
Therapies used in these phases include:
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is the major form of remission induction therapy, though it can also be used for consolidation therapy. Chemotherapy uses chemicals to kill cancer cells in your body.
- People with AML generally stay in the hospital during chemotherapy treatments because the drugs destroy many normal blood cells in the process of killing leukemia cells. If the first cycle of chemotherapy doesn't cause remission, it can be repeated.
- Targeted therapy. Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. Your leukemia cells will be tested to see if targeted therapy may be helpful for you. Targeted therapy can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy for induction therapy and consolidation therapy.
- Bone marrow transplant. A bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, may be used for consolidation therapy. A bone marrow transplant helps reestablish healthy stem cells by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with leukemia-free stem cells that will regenerate healthy bone marrow.
- Prior to a bone marrow transplant, you receive very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to destroy your leukemia-producing bone marrow. Then you receive infusions of stem cells from a compatible donor (allogeneic transplant).
- You can also receive your own stem cells (autologous transplant) if you were previously in remission and had your healthy stem cells removed and stored for a future transplant.
- Clinical trials. Some people with leukemia choose to enroll in clinical trials to try experimental treatments or new combinations of known therapies.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Acute myelogenous leukemia and Learn More about Diseases

Cavernous malformations

Pelvic organ prolapse
Dilatation of Stomach
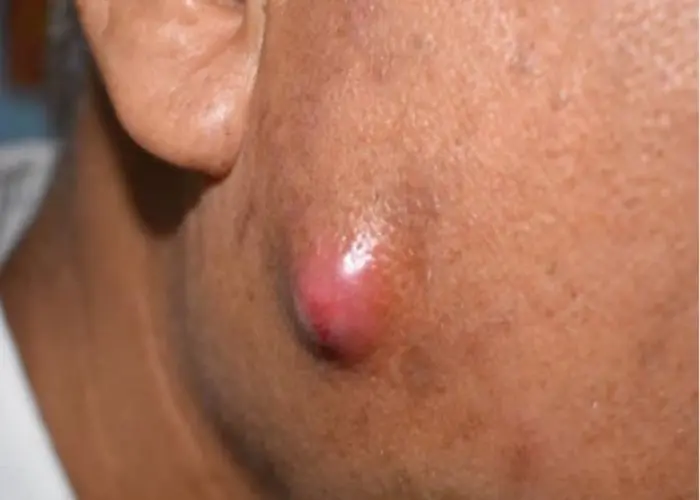
Boils (Absces or Carbuncles)

Paget's disease of the breast
Morton's neuroma

Premature ejaculation

Throat cancer
Acute myelogenous leukemia, Myelogenous leukemia symptoms, Acute myeloid leukaemia symptoms, তীব্র মাইলোজেনাস লিউকেমিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.