Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
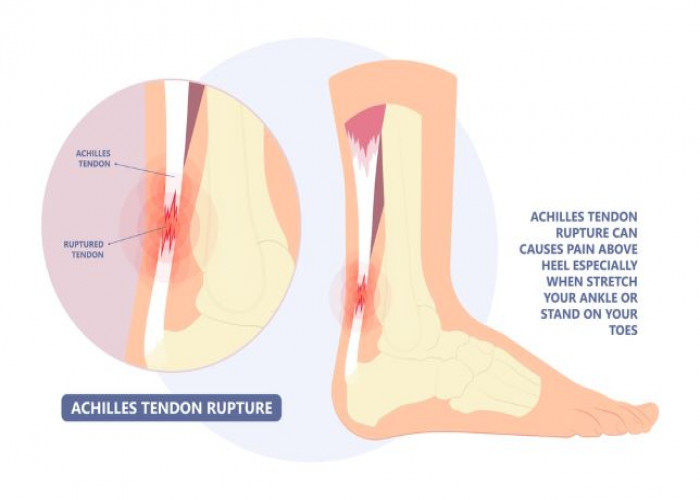
Achilles tendon rupture
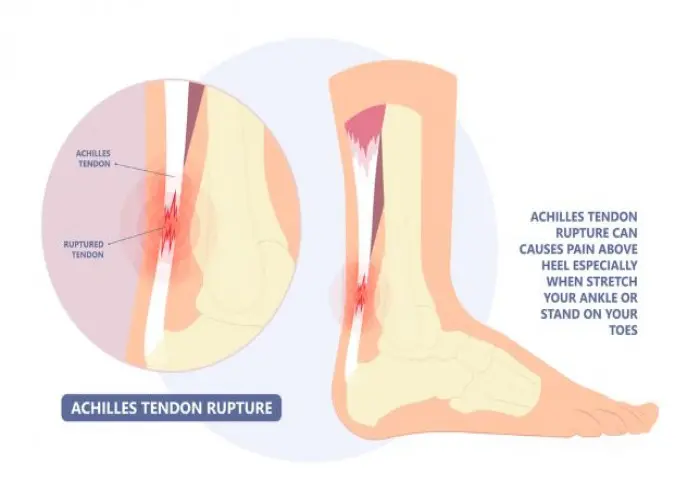
An Achilles tendon rupture is a complete or partial tear of the Achilles tendon, which is the largest tendon in the body and connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This injury is most commonly caused by sudden and forceful strain on the tendon, such as during a sudden jump or a change in direction while playing sports.
Symptoms of an Achilles tendon rupture can include sudden and sharp pain in the back of the lower leg, a popping or snapping sensation, swelling, and difficulty walking. In some cases, the affected leg may be unable to bear weight.
Diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture is typically made through a physical examination and imaging tests such as an X-ray or MRI.
Treatment for an Achilles tendon rupture may involve immobilization in a cast or boot, physical therapy, and the use of crutches. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged tendon. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the injury and other factors such as the patient's age and overall health.
Regardless of the treatment, it is important to seek prompt medical attention if you suspect you have ruptured your Achilles tendon, as failure to treat the injury can lead to long-term complications and decreased mobility.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- The feeling of having been kicked in the calf
- Pain, possibly severe, and swelling near the heel
- An inability to "push off" the injured leg when walking
- An inability to stand on the toes on the injured leg
- Popping sensation or sound at the time of injury
- Leg pain
- Achilles pain
- Achilles tendinitis
Disease Causes
Achilles tendon rupture
Your Achilles tendon helps you point your foot downward, rise on your toes and push off your foot as you walk. You rely on it virtually every time you walk and move your foot.
Rupture usually occurs in the section of the tendon situated within 2 1/2 inches (about 6 centimeters) of the point where it attaches to the heel bone. This section might be prone to rupture because blood flow is poor, which also can impair its ability to heal.
Ruptures often are caused by a sudden increase in the stress on your Achilles tendon. Common examples include:
- Increasing the intensity of sports participation, especially in sports that involve jumping
- Falling from a height
- Stepping into a hole
Disease Prevents
Achilles tendon rupture
To reduce your chance of developing Achilles tendon problems, follow these tips:
- Stretch and strengthen calf muscles. Stretch your calf until you feel a noticeable pull but not pain. Don't bounce during a stretch. Calf-strengthening exercises can also help the muscle and tendon absorb more force and prevent injury.
- Vary your exercises. Alternate high-impact sports, such as running, with low-impact sports, such as walking, biking or swimming. Avoid activities that place excessive stress on your Achilles tendons, such as hill running and jumping activities.
- Choose running surfaces carefully. Avoid or limit running on hard or slippery surfaces. Dress properly for cold-weather training, and wear well-fitting athletic shoes with proper cushioning in the heels.
- Increase training intensity slowly. Achilles tendon injuries commonly occur after an abrupt increase in training intensity. Increase the distance, duration and frequency of your training by no more than 10 percent weekly.
Disease Treatments
Treatment for a ruptured Achilles tendon often depends on your age, activity level and the severity of your injury. In general, younger and more active people, particularly athletes, tend to choose surgery to repair a completely ruptured Achilles tendon, while older people are more likely to opt for nonsurgical treatment.
Recent studies, however, have shown fairly equal effectiveness of both surgical and nonsurgical management.
Nonsurgical treatment
This approach typically involves:
- Resting the tendon by using crutches
- Applying ice to the area
- Taking over-the-counter pain relievers
- Keeping the ankle from moving for the first few weeks, usually with a walking boot with heel wedges or a cast, with the foot flexed down
Nonoperative treatment avoids the risks associated with surgery, such as infection.
However, a nonsurgical approach might increase your chances of re-rupture and recovery can take longer, although recent studies indicate favorable outcomes in people treated nonsurgically if they start rehabilitation with weight bearing early.
Surgery
The procedure generally involves making an incision in the back of your lower leg and stitching the torn tendon together. Depending on the condition of the torn tissue, the repair might be reinforced with other tendons.
Complications can include infection and nerve damage. Minimally invasive procedures reduce infection rates over those of open procedures.
Rehabilitation
After either treatment, you'll have physical therapy exercises to strengthen your leg muscles and Achilles tendon. Most people return to their former level of activity within four to six months. It's important to continue strength and stability training after that because some problems can persist for up to a year.
A type of rehabilitation known as functional rehabilitation also focuses on coordination of body parts and how you move. The purpose is to return you to your highest level of performance, as an athlete or in your everyday life.
One review study concluded that if you have access to functional rehabilitation, you might do just as well with nonsurgical treatment as with surgery. More study is needed.
Rehabilitation after either surgical or nonsurgical management is also trending toward moving earlier and progressing faster. Studies are ongoing in this area also.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Achilles tendon rupture and Learn More about Diseases
Myocardial ischemia
Seborrheic dermatitis
Septic arthritis
Dyshidrosis
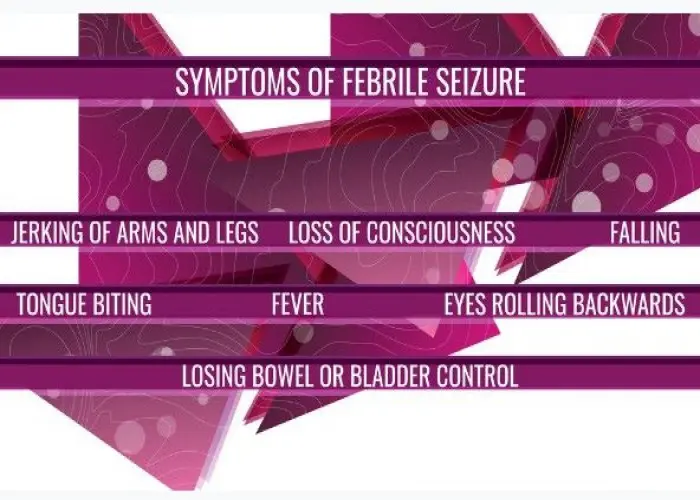
Febrile seizure
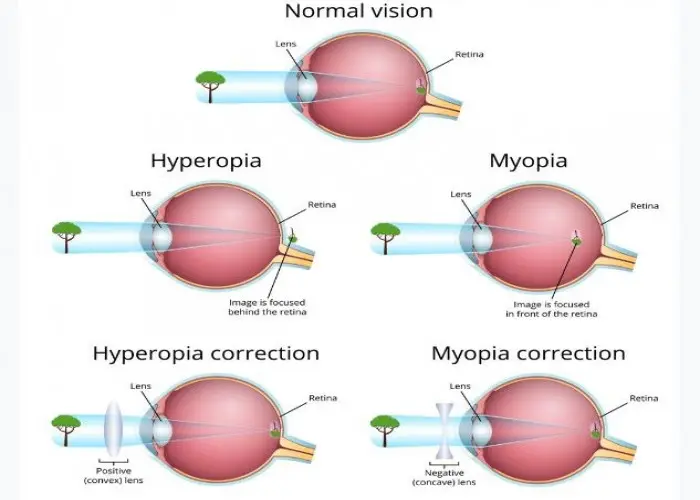
Farsightedness
Arteriovenous malformation
Fecal incontinence
Achilles tendon rupture, Torn achilles, অ্যাকিলিস টেন্ডার রাপটার
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.