Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Blood dysentery - Homeopathic remedies
Blood dysentery, also known as bacillary dysentery, is a type of bacterial infection that affects the intestines and causes severe diarrhea with the presence of blood in the stool. It is usually caused by the bacterium Shigella, which is spread through contaminated food or water, or by close contact with an infected person.
Symptoms of blood dysentery can include severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and dehydration. The diarrhea may be frequent and watery at first, but can become more severe with time, and may contain mucus and blood.
Treatment for blood dysentery typically involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. In addition, it is important to replace fluids and electrolytes lost through diarrhea to prevent dehydration, and to rest the digestive system by avoiding solid foods for a period of time.
Prevention of blood dysentery involves proper hygiene and sanitation practices, including washing hands regularly with soap and water, drinking clean and safe water, and avoiding foods that may be contaminated. If you suspect you have blood dysentery, seek medical attention immediately, as untreated cases can lead to serious complications, including kidney failure and even death.
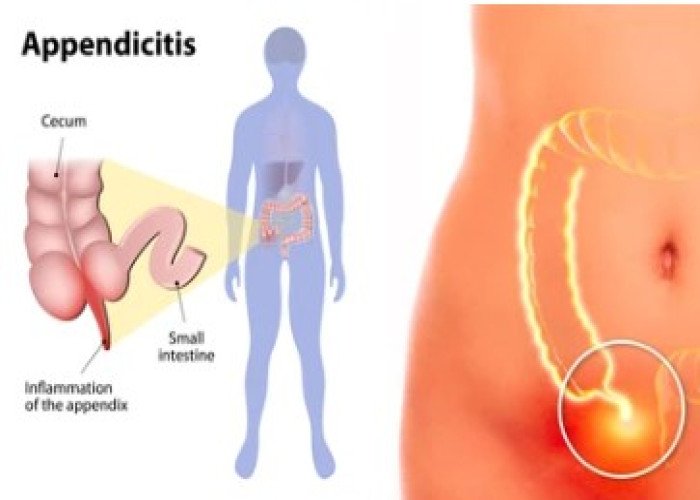
Appendicitis
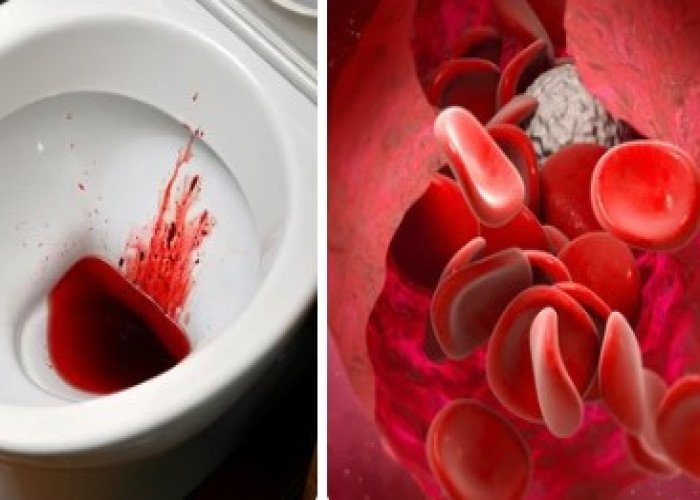
Dysentery with blood
Tumor
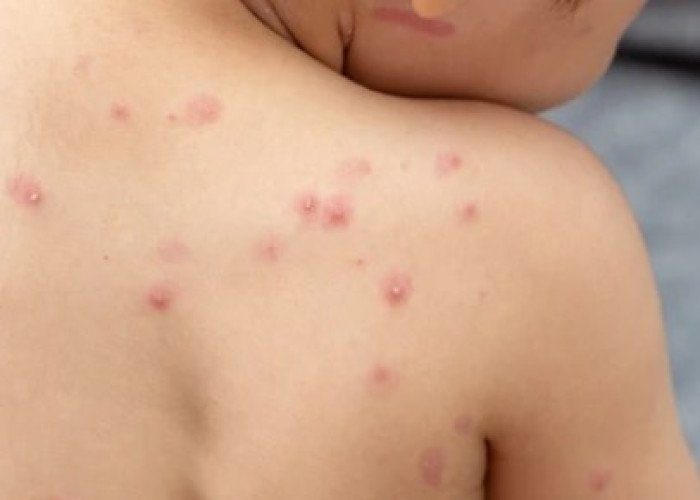
Chickenpox
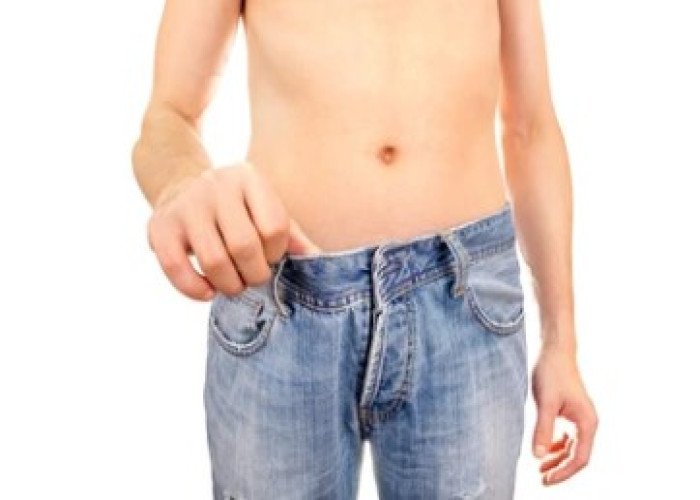

Lose flesh

Ear infection
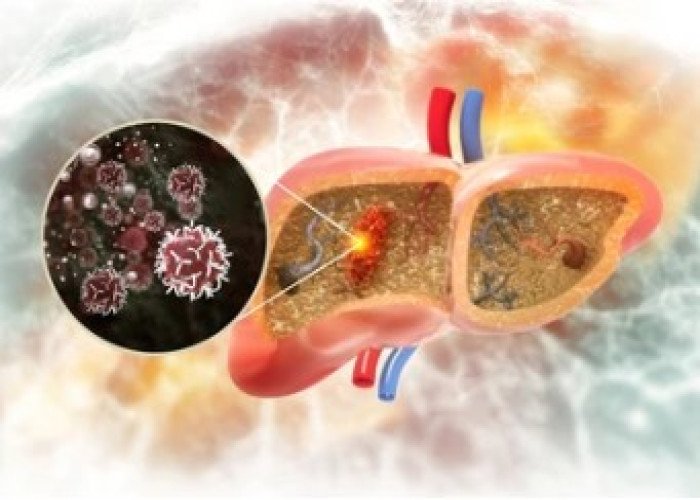
Liver cancer
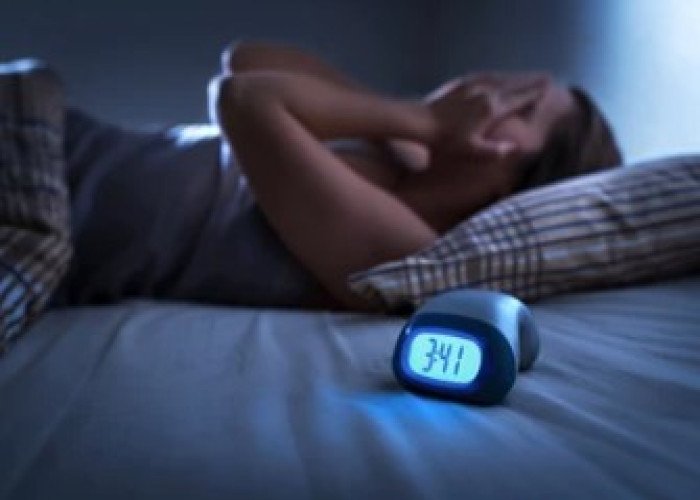

Insomnia
Blood dysentery, রক্ত আমশায়
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.