Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Ringworm - Homeopathic remedies
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. Despite its name, it is not caused by a worm but rather by a group of fungi called dermatophytes.
The symptoms of ringworm can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. The most common symptom is a ring-shaped rash with a red, scaly border and a clearer center. The rash may be itchy, and blisters may develop. In some cases, there may be hair loss or brittle nails.
Ringworm is highly contagious and can be spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal, or by sharing personal items such as clothing, towels, and combs. It can also be acquired by coming into contact with infected soil.
Treatment for ringworm typically involves antifungal medications, either topical creams or oral medications, depending on the severity of the infection. It is also important to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, avoiding sharing personal items, and keeping the affected area clean and dry.
Prevention measures include avoiding direct contact with infected individuals or animals, keeping personal items clean, and avoiding walking barefoot in areas where the infection may be present.
It is important to see a healthcare provider if you suspect you have ringworm or if your symptoms do not improve with treatment, as it can lead to complications if left untreated.

Weakness of memory

Dream of fire

Dry cough
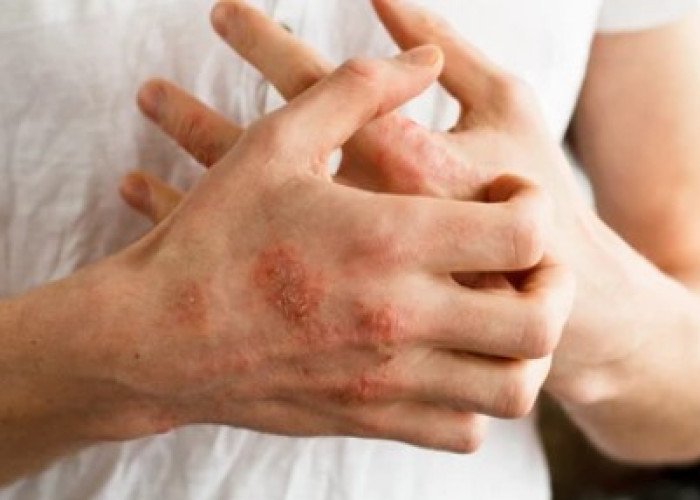
Eczema

Brain inflammation

Depressed
Meningitis
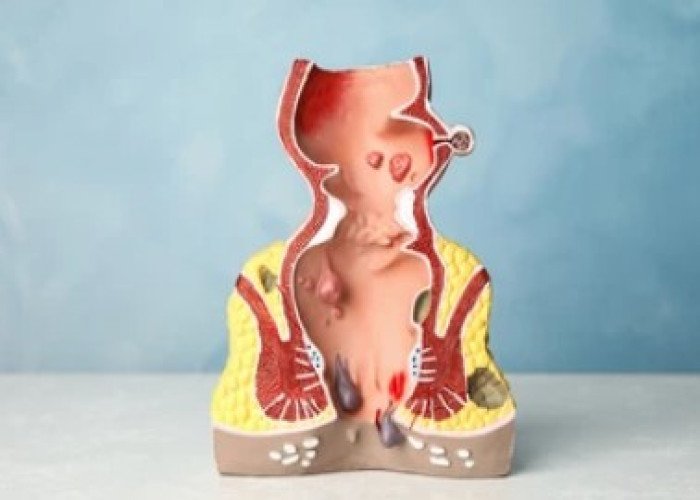
Hemorrhoids
Ringworm, দাদ
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.