 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Senile lentigines - Generics
Senile lentigines, also known as age spots or liver spots, are a common skin condition that often appears in people over the age of 50. They are flat, brown or black spots that usually appear on areas of the skin that have been exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
Senile lentigines are caused by an increase in the production of melanin, which is the pigment that gives skin its color. This increase in melanin production is usually triggered by sun exposure, but it can also be caused by other factors such as aging, hormonal changes, and genetics.
Senile lentigines are generally harmless and do not require medical treatment. However, some people may choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons. Treatment options for senile lentigines include topical creams, chemical peels, laser therapy, and cryotherapy (freezing the spots with liquid nitrogen).
Prevention of senile lentigines involves practicing good sun protection habits, such as wearing protective clothing and hats, using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and avoiding sun exposure during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.). Regular skin checks and monitoring of any changes in the appearance of the skin can also help detect any potentially cancerous growths.
Menopausal atrophic vagin...

Dietary supplements. vita...

Nutrition Hydration

Pulmonary oedema

Vitamin A deficiency
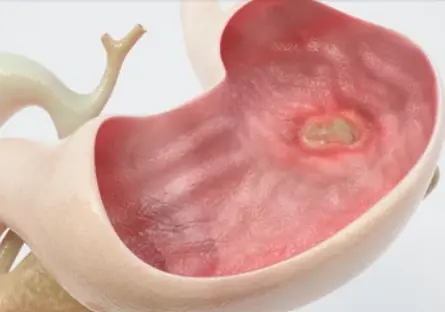
Peptic ulcer disease

Eclampsia

Irritation and discomfort...
Senile lentigines, সেনিল লেংটিগাইনস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.