 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Atopic dermatitis with secondary bacterial infections - Generics
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. People with atopic dermatitis are more susceptible to secondary bacterial infections due to the damage to the skin barrier caused by the condition. When the skin barrier is compromised, bacteria can more easily penetrate the skin and cause infections.
Symptoms of a secondary bacterial infection in a person with atopic dermatitis may include redness, swelling, and warmth around the affected area, as well as pus-filled bumps or blisters. In some cases, the area may be painful or itchy.
Treatment for atopic dermatitis with secondary bacterial infections may include topical or oral antibiotics to clear the bacterial infection. Additionally, treatment for atopic dermatitis may include topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, as well as moisturizers and other emollients to help repair the skin barrier. In some cases, oral immunosuppressants may be used to reduce inflammation and help manage the condition.
Prevention of secondary bacterial infections in people with atopic dermatitis is important and may involve avoiding scratching or rubbing the affected area, keeping the skin moisturized, and using topical antibiotics or antiseptics as directed by a healthcare provider. It is also important to maintain good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding sharing personal items such as towels and washcloths.

Osteopetrosis

Hyperhomocysteinemia

Tetanus

Productive cough

Obesity

Emergency contraception
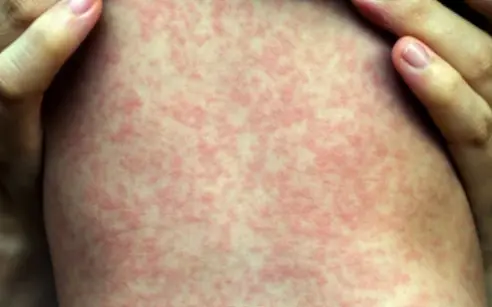
Prevention of measles
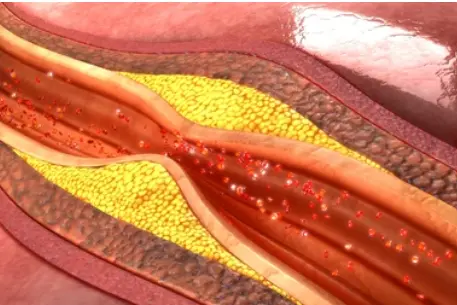
Angiography
Atopic dermatitis with secondary bacterial infections, গৌণ ব্যাকটেরিয়াল সংক্রমণের সাথে অটোপিক ডার্মাটাইটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.