 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension - Generics
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as pseudotumor cerebri, is a rare condition in which there is an increase in the pressure inside the skull that can cause symptoms such as severe headaches, vision problems, and ringing in the ears.
The exact cause of IIH is unknown, but it is thought to be related to an imbalance in the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds and cushions the brain and spinal cord. It can also be associated with obesity, certain medications, and hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms of IIH may include:
- Severe headaches, often located in the back of the head, that can be persistent or come and go.
- Vision problems, such as blurred or double vision, and in severe cases, vision loss.
- Ringing in the ears, known as tinnitus.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Neck stiffness and pain.
- Dizziness.
- Sensitivity to light.
Diagnosis of IIH may involve a physical exam, vision tests, imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans, and a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to measure the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment for IIH typically involves reducing the pressure inside the skull. This may be done through medications such as diuretics, which help reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, or through a surgical procedure called optic nerve sheath fenestration, which involves creating a small opening in the protective sheath around the optic nerve to relieve pressure.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of IIH, as untreated IIH can lead to vision loss and other serious complications.

Chronic open-angle glauco...

Grazes
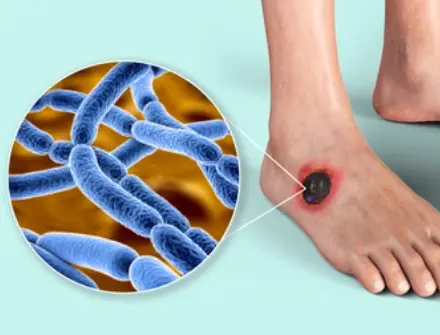
Anthrax

Caloric feeding

Agitation

Endometrium cancer

Oesophageal cancer

General anesthesia
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, ইডিওপ্যাথিক ইনট্রাক্রানিয়াল হাইপারটেনশন
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.