 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Cystoid macular edema - Generics
Cystoid macular edema (CME) is a condition in which the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for fine detail vision, becomes swollen and thickened due to the accumulation of fluid in the cyst-like spaces between the layers of the retina. This can lead to blurred or distorted vision and may affect one or both eyes.
CME can occur as a result of various underlying conditions, such as diabetes, age-related macular degeneration, uveitis (inflammation of the eye), or following eye surgery or trauma. It can also be a side effect of certain medications, such as prostaglandin analogues used in glaucoma treatment.
Treatment of CME may involve addressing the underlying cause if possible, as well as medications to reduce inflammation and swelling in the eye, such as corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In some cases, laser therapy or surgery may be necessary to resolve the swelling and restore vision.

Diverticulitis

Production of cycloplegia

Falciparum malaria

Cystitis

Flu
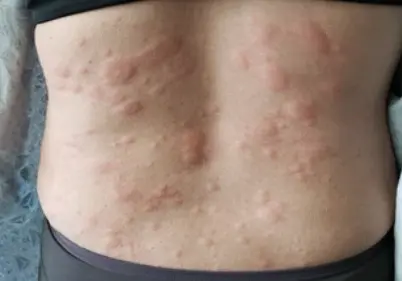
Hives

Skin healthiness

Gum disease
Cystoid macular edema, সাইস্টয়েড ম্যাকুলার এডিমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.