 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Arrhythmias - Generics
Arrhythmias are a group of heart conditions characterized by an irregular or abnormal heartbeat. They can occur when the electrical signals that control the heart's contractions become disrupted, causing the heart to beat too fast, too slow, or in an irregular pattern.
Symptoms of arrhythmias may include palpitations, which are sensations of the heart beating too fast or irregularly, shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfort, dizziness, fainting, and fatigue. Some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
Arrhythmias can be caused by a variety of factors, including heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, thyroid problems, and other underlying medical conditions. Certain medications, illegal drugs, and excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption can also trigger arrhythmias.
Treatment for arrhythmias depends on the type and severity of the condition. In some cases, no treatment may be necessary if the arrhythmia does not cause any symptoms or complications. However, if the arrhythmia is severe or causes symptoms, treatment may include medications to control the heart rate or rhythm, medical procedures such as cardioversion or ablation, or the implantation of a pacemaker or defibrillator.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have an arrhythmia, it is important to seek medical attention to receive a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Arrhythmias can have serious health consequences, including an increased risk of stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac arrest.

Mastitis

Severe burns
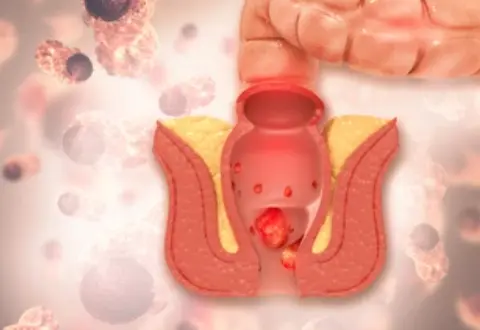
Piles

Imaging of the GI tract

Rapid eye movement behavi...

Acquired immunodeficiency...

Post-menopausal osteoporo...
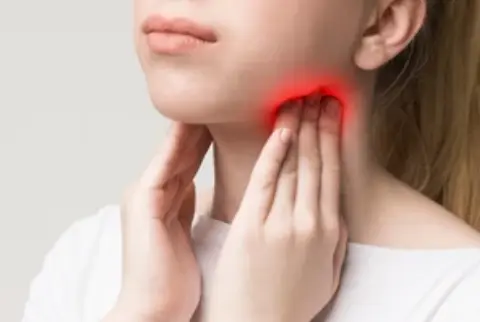
Tonsillitis
Arrhythmias, অ্যারিথমিয়াস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.