 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Square Pharmaceuticals Ltd.

Genacyn 0.30%
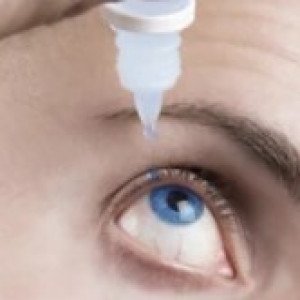
Generic for Diseases
Gentamicin sulphate actively transported across the bacterial cell membrane, binds to a specific receptor protein on the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and interferes with an initiation complex between mRNA (messenger RNA) and the 30 S subunit, inhibiting protein synthesis. DNA may be misread, thus producing nonfunctional proteins; polyribosomes are split apart and are unable to synthesize protein.
Eye drops may be absorbed following topical application to the eye. Ear drops may be absorbed following topical application to the ear, especially if the eardrum is perforated or if tissue damage is present.
Gentamicin sulphate is active against many strains of the following microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Niesseria gonorrhoea, Pseudomonus aeruginosa, and Serratia marcescens.
Blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis, acute meibomianitis, and corneal ulcers caused by susceptible organisms. Otorrhea associated with external otitis, chronic suppurative otitis media or subacute purulent otitis media; or postoperative otorrhea, such as that following fenestration, mastoidectomy or tympanoplasty.
Eye: 1-2 drops instilled in affected eye up to 6 times a day or more frequently if required (severe infections may require 1-2 drops every 15-20 minutes initially, reducing the frequency of instillation gradually as the infection is controlled).
Ear: The area should be cleaned and 2-3 drops should be instilled every 3-4 times a day and at night, or more frequently if required.
This drug is contraindicated in individuals with a history of sensitivity reaction to any of its components. Use of topical Gentamicin may occasionally allow overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi.
In patients with dermatoses treated with gentamicin, irritation (erythema and pruritus) had been reported in small number of cases. Itching, redness, swelling or other signs of irritation may develop. With the eye/ear drop bacterial and corneal ulcer have developed during treatment with gentamicin. Most frequently reported adverse reactions are ocular burning and irritation upon drug instillation, non specific conjunctivitis, conjunctival epithelial defects, and conjunctival hyperemia.
If these occurs or if irritation, sensitization develops, treatment with gentamicin should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Gentamicin ear/eye drops is not for injection. It should never be injected subconjunctivally, nor it should be directly introduced into the anterior chamber of the eye.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Consideration should be given the possibility of foetal ototoxicity when gentamicin is applied topically to large denuded areas of skin. For Gentamicin Eye/Ear Drops safety profile in pregnancy is not yet established and should be administered when considered essential.
Genacyn 0.30% and more Available Brands
Nebita Plus 2.5mg + 12...
Valoate CR 200mg
RivaXa 2.5mg
Akicin 100mg / 2m...
Calboplex
Normo-K 15gm / sac...
Jorvan 500mg
Isodex 0.18% + 4....
...
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.