Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is an infection caused by the Toxoplasma gondii parasite. It can be transmitted to humans through contact with infected cat feces, undercooked meat from infected animals, or contaminated water or soil.
Many people with toxoplasmosis have no symptoms or only mild flu-like symptoms, but the infection can be more serious in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy. In pregnant women, toxoplasmosis can cause birth defects or miscarriage.
Symptoms of toxoplasmosis may include fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. In some cases, the infection can cause eye infections or brain and nervous system problems.
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis can be done through blood tests or other laboratory tests. Treatment may not be necessary for people with mild or no symptoms, but medications can be used to treat more severe cases, particularly in people with weakened immune systems or during pregnancy.
Preventing toxoplasmosis involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands and surfaces that may be contaminated with cat feces, cooking meat to a safe temperature, and avoiding drinking untreated water or eating unwashed fruits and vegetables. Pregnant women and people with weakened immune systems should take extra precautions to avoid exposure to the parasite.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Body pain
- Yellowing of skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Seizures
- Poor coordination
- Confusion (Hallucinations)
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Fever
- Headaches
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Enlarged liver and spleen
Disease Causes
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is a single-celled parasitic organism that can infect most animals and birds. Because T. gondii infectious organisms are excreted only in cat feces, wild and domestic cats are the parasite's ultimate host.
Although you can't "catch" toxoplasmosis from an infected child or adult, you can become infected if you:
- Come into contact with cat feces that contain the parasite. You may accidentally ingest the parasites if you touch your mouth after gardening, cleaning a litter box or touching anything that has come in contact with infected cat feces. Cats who hunt or who are fed raw meat are most likely to harbor T. gondii.
- Eat or drink contaminated food or water. Lamb, pork and venison are especially likely to be infected with T. gondii. Occasionally, unpasteurized dairy products also may contain the parasite. Water contaminated with T. gondii isn't common in the United States.
- Use contaminated knives, cutting boards or other utensils. Kitchen utensils that come into contact with raw meat can harbor the parasites unless the utensils are washed thoroughly in hot, soapy water.
- Eat unwashed fruits and vegetables. The surface of fruits and vegetables may contain the parasite. To be safe, thoroughly wash and peel all produce, especially any you eat raw.
- Receive an infected organ transplant or transfused blood. In rare cases, toxoplasmosis can be transmitted through an organ transplant or blood transfusion.
When a person becomes infected with T. gondii, the parasite forms cysts that can affect almost any part of the body — often your brain and muscle tissue of different organs, including the heart.
If you're generally healthy, your immune system keeps the parasites in check. They remain in your body in an inactive state, providing you with lifelong immunity so that you can't become infected with the parasite again. But if your immune system is weakened by disease or certain medications, the infection can be reactivated, leading to serious complications.
Disease Prevents
Toxoplasmosis
Certain precautions can help prevent toxoplasmosis:
- Wear gloves when you garden or handle soil. Wear gloves whenever you work outdoors and wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water afterward.
- Don't eat raw or undercooked meat. Meat, especially lamb, pork and beef, can harbor toxoplasma organisms. Don't taste meat before it's fully cooked. Avoid raw cured meat.
- Wash kitchen utensils thoroughly. After preparing raw meat, wash cutting boards, knives and other utensils in hot, soapy water to prevent cross-contamination of other foods. Wash your hands after handling raw meat.
- Wash all fruits and vegetables. Scrub fresh fruits and vegetables, especially if you plan to eat them raw. Remove peels when possible, but only after washing.
- Don't drink unpasteurized milk. Unpasteurized milk and other dairy products may contain toxoplasma parasites.
- Cover children's sandboxes. If you have a sandbox, cover it when your children aren't playing in it to keep cats from using it as a litter box.
For cat lovers
If you're pregnant or otherwise at risk of toxoplasmosis or its complications, take these steps to protect yourself:
- Help your cat stay healthy. Keep your cat indoors and feed it dry or canned cat food, not raw meat. Cats can become infected after eating infected prey or undercooked meat that contains the parasite.
- Avoid stray cats or kittens. Although all stray animals need good homes, it's best to let someone else adopt them. Most cats don't show signs of T. gondii infection, and although they can be tested for toxoplasmosis, it may take up to a month to get the results.
- Have someone else clean your cat's litter box. If that's not possible, wear gloves and a face mask to change the litter. Then wash your hands well. Change the litter daily so that excreted cysts don't have time to become infectious.
Disease Treatments
Most healthy people don't require toxoplasmosis treatment. But if you're otherwise healthy and have signs and symptoms of acute toxoplasmosis, your doctor may prescribe the following drugs:
- Pyrimethamine (Daraprim). This medication, typically used for malaria, is a folic acid antagonist. It may prevent your body from absorbing the B vitamin folate (folic acid, vitamin B-9), especially when you take high doses over a long period. For that reason, your doctor may recommend taking additional folic acid.
- Other potential side effects of pyrimethamine include bone marrow suppression and liver toxicity.
- Sulfadiazine. This antibiotic is used with pyrimethamine to treat toxoplasmosis.
Treating people with HIV/AIDS
If you have HIV/AIDS, the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis is also pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine, with folinic acid (leucovorin). An alternative is pyrimethamine taken with clindamycin (Cleocin).
Treating pregnant women and babies
If you're pregnant and infected with toxoplasmosis, treatment may vary depending on where you receive medical care.
If infection occurred before the 16th week of pregnancy, you may receive the antibiotic spiramycin. Use of this drug may reduce your baby's risk of neurological problems from congenital toxoplasmosis. Spiramycin is routinely used to treat toxoplasmosis in Europe, but is still considered experimental in the United States.
If infection occurred after the 16th week of pregnancy, or if tests show that your unborn child has toxoplasmosis, you may be given pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine and folinic acid (leucovorin). Your doctor will help you determine the optimal treatment.
If your infant has toxoplasmosis or is likely to have it, treatment with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine and folinic acid (leucovorin) is recommended. Your baby's doctor will need to monitor your baby while he or she is taking these medications.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Toxoplasmosis and Learn More about Diseases

Dumping syndrome

Infertility (Sterility)
Dilatation of Stomach
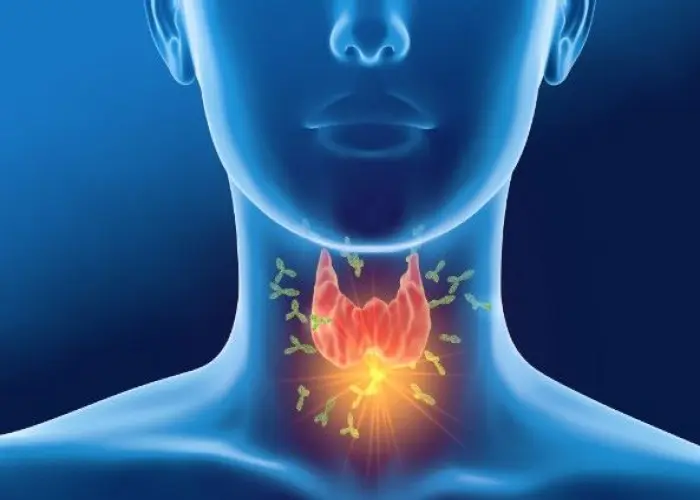
Hashimoto's disease
Lynch syndrome
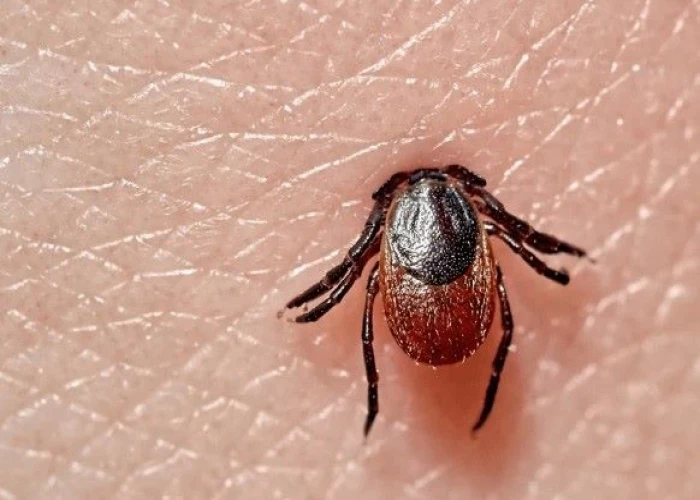

Lyme disease

Gas and gas pains
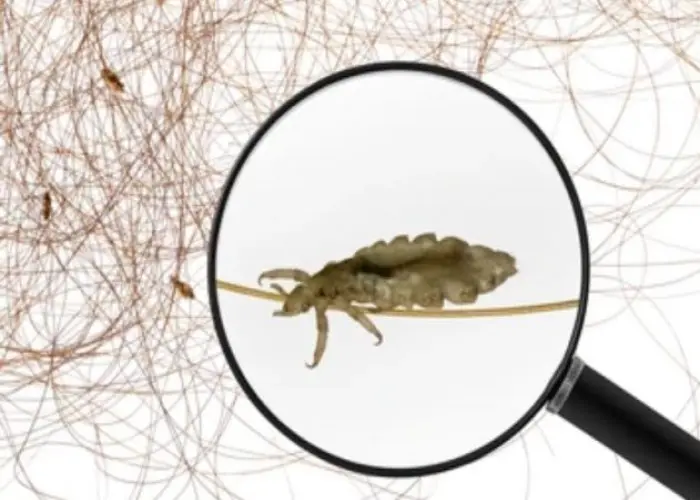

Body lice
toxoplasmosis, টক্সোপ্লাজমোসিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.