 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Sick sinus syndrome

Sick sinus syndrome (SSS) is a medical condition that affects the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is the natural pacemaker of the heart. The SA node is responsible for setting the heart's rhythm and regulating the heartbeat. In SSS, the SA node does not function properly, leading to abnormal heart rhythms or even pauses in the heartbeat.
Symptoms of sick sinus syndrome may include:
- Fainting or feeling dizzy
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Palpitations (an irregular or pounding heartbeat)
Sick sinus syndrome can occur in people of any age, but it is most common in older adults. The condition may be caused by a number of factors, including age-related changes to the heart, certain medications, or underlying heart disease.
Treatment for sick sinus syndrome may involve medications to control the heart rate or rhythm, or a pacemaker may be implanted to help regulate the heartbeat. In some cases, treatment may involve surgery or other medical procedures to correct underlying heart problems.
If you experience any symptoms of sick sinus syndrome, it is important to see your healthcare provider for an evaluation and diagnosis. With appropriate treatment, many people with sick sinus syndrome can manage their symptoms and lead active, healthy lives.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Dizziness (vertigo)
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or faintness
- Fainting (syncope)
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Chest pain
- Confusion (Hallucinations)
- Slow pulse (bradycardia)
- Rapid fluttering heartbeats (palpitations)
Disease Causes
Sick sinus syndrome
Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper (atria) and two lower (ventricles). The rhythm of your heart is normally controlled by the sinus node, an area of specialized cells in the right upper heart chamber (atrium).
This natural pacemaker produces electrical signals that trigger each heartbeat. From the sinus node, electrical signals travel across the atria to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood to your lungs and body.
If you have sick sinus syndrome, your sinus node isn't working properly, causing your heart rate to be too slow (bradycardia), too fast (tachycardia) or irregular.
Problems of the sinus node include the following:
- Sinus bradycardia. The sinus node produces an electrical charge at a slower rate than normal.
- Sinus arrest. Signals from the sinus node pause, causing skipped beats.
- Sinoatrial exit block. Signals to the upper heart chambers are slowed or blocked, causing a pause or skipped beats.
- Chronotropic incompetence. The heart rate is normal at rest, but doesn't increase with physical activity.
- Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome. The heart rate alternates between abnormally slow and fast rhythms, usually with a long pause (asystole) between heartbeats.
Disease Prevents
Disease Treatments
The primary treatment goals are to reduce or eliminate symptoms and to manage and treat any other health conditions that may be contributing to sick sinus syndrome.
If you don't have symptoms, your doctor may recommend regularly scheduled exams to monitor your condition. For most people with symptoms, the treatment is an implanted electronic pacemaker. If your symptoms are mild or infrequent, the decision to use a pacemaker will depend on results of ECG exams, your overall health, and the risk of more-serious problems.
Medication changes
Your doctor will likely check your current medications to see if any could be interfering with the function of your sinus node, including some medications used to treat high blood pressure or heart disease. Your doctor may adjust these medications or prescribe alternatives.
Pacing the heart
Most people with sick sinus syndrome eventually need a permanent artificial pacemaker to maintain a regular heartbeat. This small, battery-powered electronic device is implanted under the skin near your collarbone during a minor surgical procedure. The pacemaker is programmed to stimulate or "pace" your heart as needed to keep it beating normally.
The type of pacemaker you need depends on the type of irregular heart rhythm you have. Some rhythms can be treated with a single-chamber pacemaker, which uses only one wire (lead) in the right atrium to pace the heart rate. However, most people with sick sinus syndrome benefit from dual-chamber pacemakers. One lead in the right atrium paces the upper chambers, and one lead in the right ventricle paces the lower chambers.
You'll be able to resume normal or near-normal activities after you recover from pacemaker implantation surgery. The risk of complications, such as swelling or infection in the area where the pacemaker was implanted, is small.
Additional treatments for fast heart rate
If you have a rapid heart rate as part of your sick sinus syndrome, you may need additional treatments to control these rhythms:
- Medications. If you have a pacemaker and your heart rate is still too fast, your doctor may prescribe medications to prevent or to slow down fast rhythms. If you have atrial fibrillation or other abnormal heart rhythms that increase your risk of stroke, you may need a blood-thinning medicine, such as warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven), dabigatran (Pradaxa) or other similar medications.
- AV node ablation. This procedure also can control fast heart rhythms in people with pacemakers. It involves applying radiofrequency energy through a long, thin tube (catheter) to destroy (ablate) the tissue around the atrioventricular (AV) node between the atria and the ventricles. This stops fast heart rhythms from reaching the ventricles and causing problems.
- Cardiac ablation for atrial fibrillation. This procedure is similar to AV node ablation. However, in this case, ablation targets heart tissues that can lead to atrial fibrillation. This actually eliminates atrial fibrillation itself, rather than just preventing it from reaching the ventricles.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Sick sinus syndrome and Learn More about Diseases
Hepatitis C

Carpal tunnel syndrome
Arteriovenous fistula

Giant cell arteritis

Pectus carinatum
Kidney stones
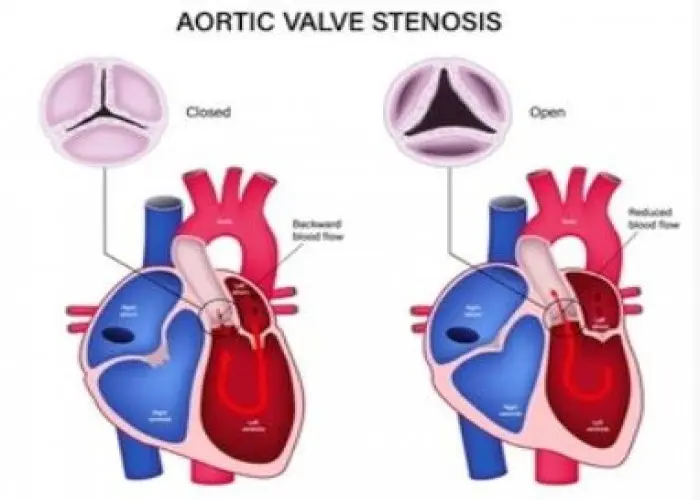
Aortic valve stenosis
Small bowel prolapse (enterocele)
sick sinus syndrome, সিক সাইনাস সিন্ড্রোম
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
