 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Lead poisoning
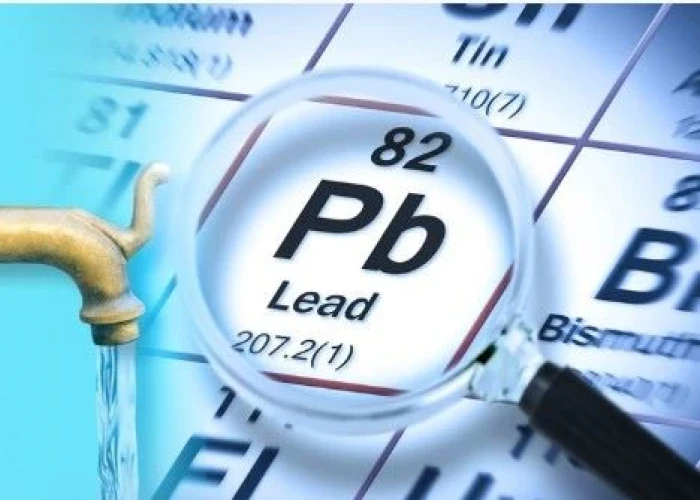

Lead poisoning is a condition that occurs when a person has high levels of lead in their body. Lead is a toxic metal that can cause serious health problems, especially in children, who are more vulnerable to its effects.
Lead poisoning can occur when lead is ingested or inhaled. Sources of lead exposure include old paint in homes, contaminated soil, dust, and some types of pottery or toys. Children may also be exposed to lead through water from lead pipes or plumbing fixtures.
Symptoms of lead poisoning can vary depending on the level of exposure, but may include:
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Anemia
- Behavioral problems
- Developmental delays in children
- Seizures or coma in severe cases
Diagnosis of lead poisoning may involve a blood test to measure the level of lead in the body. Treatment may involve removing the source of lead exposure, such as lead paint or contaminated soil, and providing medication to reduce the level of lead in the body. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide treatment and support.
Preventing lead poisoning involves identifying potential sources of lead exposure, such as lead paint or contaminated soil, and taking steps to reduce or eliminate exposure. This may involve testing for lead in homes, using lead-free paint, and avoiding the use of certain products that may contain lead. It is important for parents and caregivers to be aware of the risks of lead exposure and take steps to protect children from potential sources of exposure.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Learning problems
- Chest pain, often after exercising
- Headaches
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Seizures
- Decreased hearing
- Constipation
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdomen pain
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
- Lead poisoning
Disease Causes
Lead poisoning
Lead is a metal that occurs naturally in the earth's crust, but human activity — mining, burning fossil fuels and manufacturing — has caused it to become more widespread. Lead was also once used in paint and gasoline and is still used in batteries, solder, pipes, pottery, roofing materials and some cosmetics.
Lead in paint
Lead-based paints for homes, children's toys and household furniture have been banned in the United States since 1978. But lead-based paint is still on walls and woodwork in many older homes and apartments. Most lead poisoning in children results from eating chips of deteriorating lead-based paint.
Water pipes and imported canned goods
Lead pipes, brass plumbing fixtures and copper pipes soldered with lead can release lead particles into tap water. Lead solder in food cans, banned in the United States, is still used in some countries.
Other sources of lead exposure
Lead sometimes can also be found in:
- Soil. Lead particles from leaded gasoline or paint settle on soil and can last years. Lead-contaminated soil is still a major problem around highways and in some urban settings. Some soil close to walls of older houses contains lead.
- Household dust. Household dust can contain lead from lead paint chips or from contaminated soil brought in from outside.
- Pottery. Glazes found on some ceramics, china and porcelain can contain lead that can leach into food served or stored in the pottery.
- Toys. Lead is sometimes found in toys and other products produced abroad.
- Cosmetics. Tiro, an eye cosmetic from Nigeria, has been linked to lead poisoning. Kohl is another eye makeup that may contain lead.
- Herbal or folk remedies. Lead poisoning has been linked to greta and azarcon, traditional Hispanic medicines, as well as some from India, China and other countries.
- Mexican candy. Tamarind, an ingredient used in some candies made in Mexico, might contain lead.
- Lead bullets. Time spent at firing ranges can lead to exposure.
- Occupations. People are exposed to lead and can bring it home on their clothes when they work in auto repair, mining, pipe fitting, battery manufacturing, painting, construction and certain other fields.
Disease Prevents
Lead poisoning
Simple measures can help protect you and your family from lead poisoning:
- Wash hands and toys. To help reduce hand-to-mouth transfer of contaminated dust or soil, wash your children's hands after outdoor play, before eating and at bedtime. Wash their toys regularly.
- Clean dusty surfaces. Clean your floors with a wet mop and wipe furniture, windowsills and other dusty surfaces with a damp cloth.
- Remove shoes before entering the house. This will help keep lead-based soil outside.
- Run cold water. If you have older plumbing containing lead pipes or fittings, run your cold water for at least a minute before using. Don't use hot tap water to make baby formula or for cooking.
- Prevent children from playing on soil. Provide them with a sandbox that's covered when not in use. Plant grass or cover bare soil with mulch.
- Eat a healthy diet. Regular meals and good nutrition might help lower lead absorption. Children especially need enough calcium, vitamin C and iron in their diets to help keep lead from being absorbed.
- Keep your home well maintained. If your home has lead-based paint, check regularly for peeling paint and fix problems promptly. Try not to sand, which generates dust particles that contain lead.
Disease Treatments
The first step in treating lead poisoning is to remove the source of the contamination. If you can't remove lead from your environment, you might be able to reduce the likelihood that it will cause problems.
For instance, sometimes it's better to seal in rather than remove old lead paint. Your local health department can recommend ways to identify and reduce lead in your home and community.
For children and adults with relatively low lead levels, simply avoiding exposure to lead might be enough to reduce blood lead levels.
Treating higher levels
For more-severe cases, your doctor might recommend:
- Chelation therapy. In this treatment, a medication given by mouth binds with the lead so that it's excreted in urine. Chelation therapy might be recommended for children with a blood level of 45 mcg/dL or greater and adults with high blood levels of lead or symptoms of lead poisoning.
- EDTA chelation therapy. Health care providers treat adults with lead levels greater than 45 mcg/dL of blood and children who can't tolerate the drug used in conventional chelation therapy most commonly with a chemical called calcium disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). EDTA is given by injection.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Lead poisoning and Learn More about Diseases
Neurofibromatosis

Chlamydia trachomatis

Anthrax
Hemangioma

Alcohol poisoning

Priapism

Type 1 diabetes in children

Temporal lobe seizure
lead poisoning, সীসা বিষক্রিয়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
