Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Epididymitis
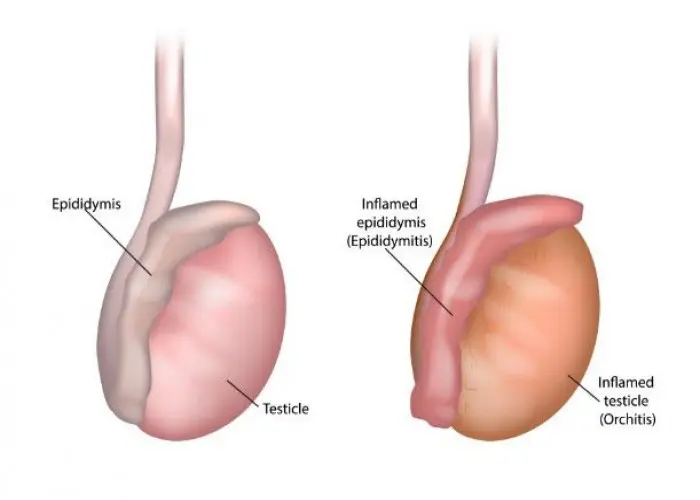
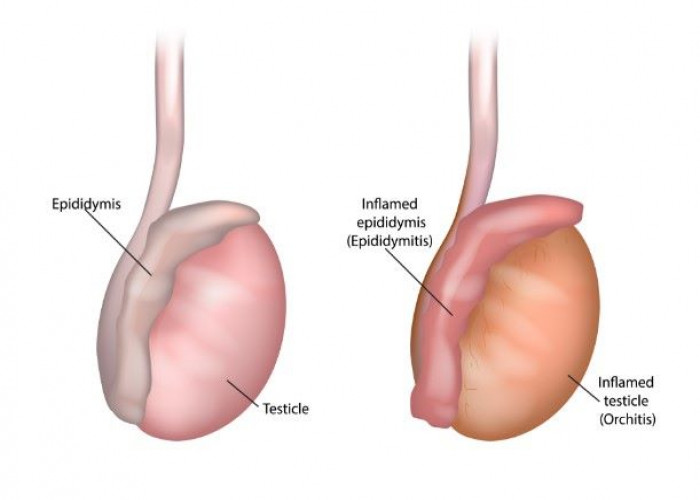
Epididymitis is a medical condition in which the epididymis, a structure in the male reproductive system that sits behind the testicles and stores and transports sperm, becomes inflamed. This can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the scrotum.
The most common cause of epididymitis is a bacterial infection, which can be sexually transmitted or arise from other sources such as urinary tract infections, prostate infections, or the spread of infection from other parts of the body. Non-infectious causes, such as trauma or obstruction of the epididymal ducts, can also lead to epididymitis.
Symptoms of epididymitis may include pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the scrotum, as well as fever and chills. In some cases, there may be discharge from the penis or pain during urination. Prompt evaluation and treatment are important to prevent complications such as abscess formation or infertility.
Treatment for epididymitis typically involves antibiotics to treat the underlying infection, as well as pain relievers and measures to reduce swelling such as elevation of the scrotum and the use of cold packs. Sexual partners may also need to be treated. If complications such as abscesses or testicular infarction occur, surgery may be needed.
Prevention of epididymitis includes practicing safe sex, prompt treatment of urinary tract infections or other infections that can spread to the epididymis, and careful attention to genital hygiene.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Swollen testicle
- Testicular pain
- Discharge from penis
- Lower abdomen pain
- Fever
Disease Causes
Epididymitis
Causes of epididymitis include:
- STIs. Gonorrhea and chlamydia are the most common causes of epididymitis in young, sexually active men.
- Other infections. Bacteria from a urinary tract or prostate infection might spread from the infected site to the epididymis. Also, viral infections, such as the mumps virus, can result in epididymitis.
- Urine in the epididymis (chemical epididymitis). This condition occurs when urine flows backward into the epididymis, possibly because of heavy lifting or straining.
- Trauma. A groin injury can cause epididymitis.
- Tuberculosis. Rarely, epididymitis can be caused by tuberculosis infection.
Disease Prevents
Epididymitis
To help protect against STIs that can cause epididymitis practice safer sex.
If you have recurrent urninary tract infections or other risk factors for epididymitis, your doctor might discuss with you other ways of preventing a recurrence.
Disease Treatments
Antibiotics are needed to treat bacterial epididymitis and epididymo-orchitis. If the cause of the bacterial infection is an STI, your sexual partner also needs treatment. Take the entire course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor, even if your symptoms clear up sooner, to ensure that the infection is gone.
You should start to feel better within 48 to 72 hours of starting an antibiotic. Resting, supporting the scrotum with an athletic supporter, applying ice packs and taking pain medication can help relieve discomfort.
Your doctor is likely to recommend a follow-up visit to check that the infection has cleared.
Surgery
If an abscess has formed, you might need surgery to drain it. Sometimes, all or part of the epididymis needs to be removed surgically (epididymectomy). Surgery might also be considered if epididymitis is due to underlying physical abnormalities.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Epididymitis and Learn More about Diseases
Popliteal artery entrapment syndrome

Eyestrain

Concussion

TMJ disorders

Interstitial cystitis
Adnexal tumors

Coarctation of the aorta

Vulvar cancer
epididymitis, এপিডিডাইমিটিস
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.