Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Boils (Absces or Carbuncles)
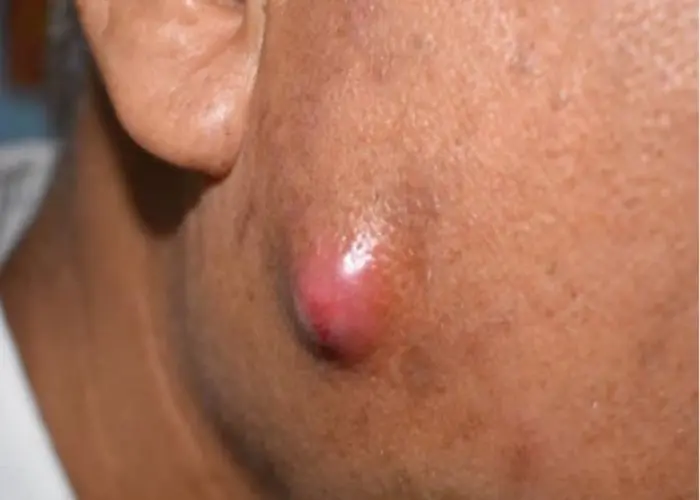
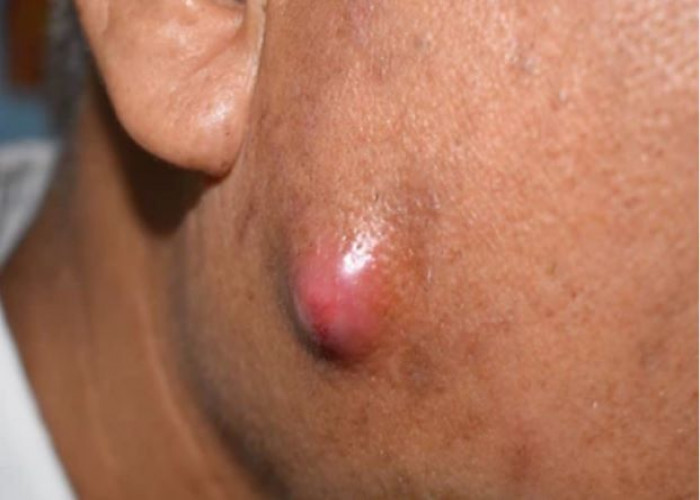
Boils, also known as abscesses or carbuncles, are painful, pus-filled bumps that can develop on the skin. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection that affects a hair follicle or oil gland. Boils can occur anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, and buttocks. Treatment options may include applying warm compresses to the affected area to help the boil come to a head and drain, cleaning the area with antiseptic solutions, taking antibiotics if the infection is severe, or lancing the boil in some cases to drain the pus. It is important to seek medical attention if the boil is large, persistent, or associated with other symptoms such as fever, redness, or swelling. This can help prevent potential complications, such as the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Boils in armpits
- Skin bumps
- A painful, red bump that starts out small and can enlarge to more than 2 inches (5 centimeters)
- An increase in the size of the bump over a few days as it fills with pus
- Development of a yellow-white tip that eventually ruptures and allows the pus to drain out
Disease Causes
Boils and carbuncles
Most boils are caused by Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacterium commonly found on the skin and inside the nose. A bump forms as pus collects under the skin. Boils sometimes develop at sites where the skin has been broken by a small injury or an insect bite, which gives the bacteria easy entry.
Disease Prevents
Boils and carbuncles
It's not always possible to prevent boils, especially if you have a weakened immune system. But the following measures may help you avoid staph infections:
- Wash your hands regularly with mild soap. Or use an alcohol-based hand rub often. Careful hand-washing is your best defense against germs.
- Keep wounds covered. Keep cuts and abrasions clean and covered with sterile, dry bandages until they heal.
- Avoid sharing personal items. Don't share towels, sheets, razors, clothing, athletic equipment and other personal items. Staph infections can spread via objects, as well as from person to person. If you have a cut or sore, wash your towels and linens using detergent and hot water with added bleach, and dry them in a hot dryer.
Disease Treatments
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Phenoxymethyl Penicillin [Penicillin V]
For inflammation. 1 250 mg pill every 6 hours.
-
Oxytetracycline
1 capsule every 6 hours.
-
Flucloxacillin Sodium
1 tablet/1 spoon every 6 hours for 7 days. The dose can be doubled if necessary.
-
Cephalexin
1 capsule every 6 hours.
-
Doxycycline Hydrochloride
1 capsule 2 times a day.
-
Cefaclor Monohydrate
1 after 8 hours. The dose can be doubled if needed.
-
Aspirin
Medicines like aspirin for pain.
-
Paracetamol
1 tablet 3 times a day.
-
Naproxen Sodium
Medicines containing naproxen for pain.
-
Ranitidine Hydrochloride
Medicines containing ranitidine for stomach gas.
1 pill in the morning and 1 pill at night after food.
-
Erythromycin (Oral)
For those who do not tolerate penicillin or are likely to have a reaction to penicillin, erythromycin is recommended.
-
Vitamin B complex
1 pill 1/2 time a day.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
-
Belladonna
3X power.
-
Hepar sulphur
6, 30 power.
-
Silicea
30, 200 power.
-
Mercurius solubilis
6, 30 power.
-
Phosphorus
6, 30 power.
-
Lachesis
200 power.
Disease yoga
Boils (Absces or Carbuncles) and Learn More about Diseases
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
Sarcoidosis

Trigger finger

Cardiogenic shock
Ganglion cyst

Vascular dementia
Bile reflux

Migraine
Boils, Absces, Boils on skin, Carbuncles, ফোঁড়া
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.