 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Allergies
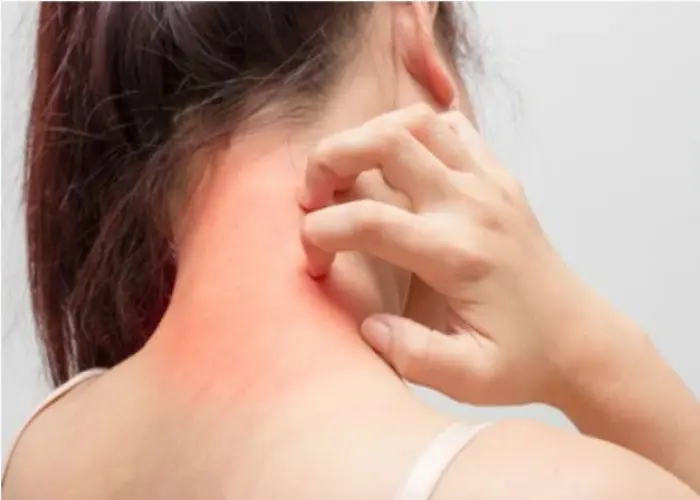
Allergies are a common condition in which the body's immune system reacts to substances that are typically harmless to most people. These substances, known as allergens, can include things like pollen, pet dander, certain foods, insect stings, and medications.
Symptoms of allergies may include:
- Sneezing
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Itchy, watery eyes
- Hives or skin rashes
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea (with food allergies)
- Chest tightness, wheezing, or coughing (with asthma)
In some cases, an allergic reaction can be severe and life-threatening, known as anaphylaxis. Symptoms of anaphylaxis may include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and loss of consciousness.
Treatment for allergies depends on the type and severity of the reaction. In some cases, avoiding the allergen or taking over-the-counter or prescription medications, such as antihistamines or decongestants, may be effective. In more severe cases, immunotherapy (allergy shots) may be recommended.
If you think you may have an allergy, it's important to see a doctor. They can perform tests to determine the cause of your symptoms and help develop a plan to manage your allergies.
Research Papers
Disease Signs and Symptoms
- Conjoined twins
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or faintness
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Shock with a severe drop in blood pressure
- Abdomen bloating
- Swollen facial
- Skin rash
- Cough, chest tightness, wheezing or shortness of breath
- Itching or hives all over the body
- Hives
- Swollen eye (Conjunctivitis)
- Runny nose
- Itchy nose, roof of mouth or throat
- Tingling in mouth
- Nausea or vomiting
Disease Causes
Allergies
An allergy starts when your immune system mistakes a normally harmless substance for a dangerous invader. The immune system then produces antibodies that remain on the alert for that particular allergen. When you're exposed to the allergen again, these antibodies can release a number of immune system chemicals, such as histamine, that cause allergy symptoms.
Common allergy triggers include:
- Airborne allergens, such as pollen, animal dander, dust mites and mold
- Certain foods, particularly peanuts, tree nuts, wheat, soy, fish, shellfish, eggs and milk
- Insect stings, such as from a bee or wasp
- Medications, particularly penicillin or penicillin-based antibiotics
- Latex or other substances you touch, which can cause allergic skin reactions
Disease Prevents
Allergies
Preventing allergic reactions depends on the type of allergy you have. General measures include the following:
- Avoid known triggers. Even if you're treating your allergy symptoms, try to avoid triggers. If, for instance, you're allergic to pollen, stay inside with windows and doors closed when pollen is high. If you're allergic to dust mites, dust and vacuum and wash bedding often.
- Keep a diary. When trying to identify what causes or worsens your allergic symptoms, track your activities and what you eat, when symptoms occur and what seems to help. This may help you and your doctor identify triggers.
- Wear a medical alert bracelet. If you've had a severe allergic reaction, a medical alert bracelet (or necklace) lets others know that you have a serious allergy in case you have a reaction and you're unable to communicate.
Disease Treatments
Allergy treatments include:
- Allergen avoidance. Your doctor will help you take steps to identify and avoid your allergy triggers. This is generally the most important step in preventing allergic reactions and reducing symptoms.
- Medications. Depending on your allergy, medications can help reduce your immune system reaction and ease symptoms. Your doctor might suggest over-the-counter or prescription medication in the form of pills or liquid, nasal sprays, or eyedrops.
- Immunotherapy. For severe allergies or allergies not completely relieved by other treatment, your doctor might recommend allergen immunotherapy. This treatment involves a series of injections of purified allergen extracts, usually given over a period of a few years.
- Another form of immunotherapy is a tablet that's placed under the tongue (sublingual) until it dissolves. Sublingual drugs are used to treat some pollen allergies.
- Emergency epinephrine. If you have a severe allergy, you might need to carry an emergency epinephrine shot at all times. Given for severe allergic reactions, an epinephrine shot (Auvi-Q, EpiPen, others) can reduce symptoms until you get emergency treatment.
Disease Diagnoses
Disease Allopathic Generics
-
Chlorpheniramine Maleate
Adults take 1 pill 3-4 times a day.
-
Promethazine Hydrochloride
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Pheniramine Maleate
1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Dimethothiazine Mesylate
Adults take 1 pill 3 times a day.
-
Mebhydrolin Napadisylate
1/2 pill 2/3 times a day according to age.
-
Cetirizine Hydrochloride
Over 12 years 1 tablet (10mg) 1 time a day or syrup 1 spoon (5mg) 2 times a day.
-
Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride
1 time per day.
-
Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride
1 each 3 times a day. The maximum dose is 200mg in divided doses. Cannot be given below 6 years.
-
Loratadine
0+0+1.
-
Desloratadine
0+0+1.
Disease Ayurvedic Generics
Disease Homeopathic Generics
Disease yoga
Allergies and Learn More about Diseases

Reye's syndrome
Congenital myasthenic syndromes

Ascites

Bad breath
Post-vasectomy pain syndrome
Peritonitis
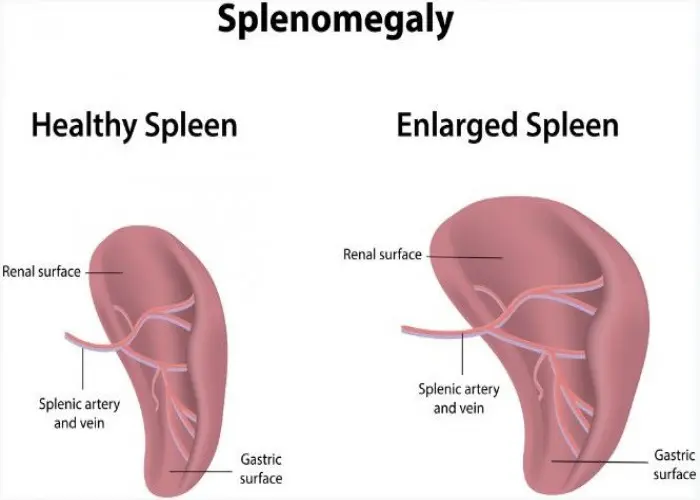
Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
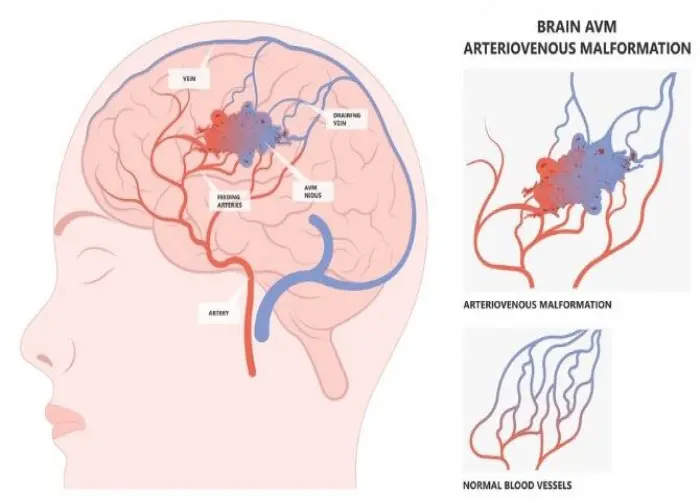
Intracranial venous malformations
Allergies, Anaphylaxis, Rhinitis, এলার্জি
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.
