 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Growth retardation - Homeopathic remedies
Growth retardation refers to a condition in which a child is significantly smaller in height and weight than other children of the same age and gender. The child's growth rate is slower than normal and he or she may not reach the expected height and weight milestones.
Growth retardation can have several causes, including genetic factors, poor nutrition, chronic diseases, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications. It can also be a result of intrauterine growth restriction, which occurs when a baby does not receive adequate nutrients and oxygen during pregnancy.
Early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause of growth retardation are essential to prevent complications such as delayed puberty, skeletal deformities, and developmental delays. Treatment may involve addressing nutritional deficiencies, hormone replacement therapy, medication, or surgery. A pediatrician or endocrinologist can help diagnose and manage growth retardation.
Sciatica
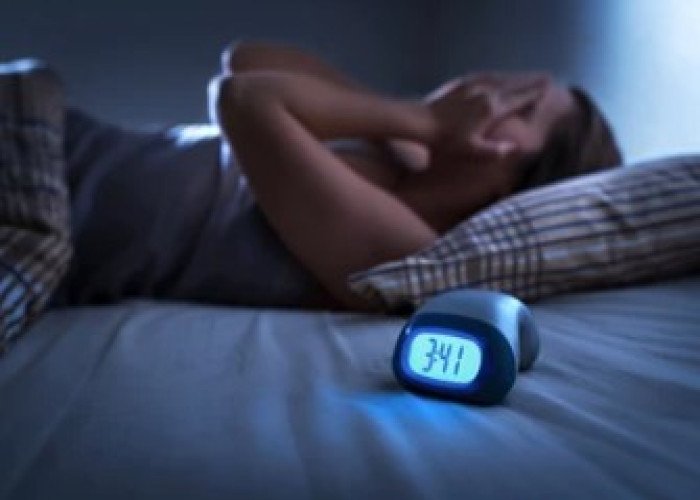

Insomnia

Water dream
Nodule
Blood dysentery
Lot of urine

Fear in dark

Anxiety
Growth retardation, বৃদ্ধির খর্বতা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.

