 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Blood clots in brain - Homeopathic remedies
Blood clots in the brain, also known as cerebral embolism or cerebral thrombosis, can cause a variety of symptoms and can be a serious medical emergency.
Blood clots in the brain can form when a blood vessel in the brain becomes damaged or blocked, causing a disruption in blood flow to the brain. This can be caused by a number of factors, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity, atherosclerosis, or certain medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
Symptoms of blood clots in the brain can include sudden and severe headaches, dizziness or loss of balance, confusion or difficulty speaking or understanding, vision changes, weakness or numbness on one side of the body, or seizures.
Immediate medical attention is necessary for blood clots in the brain. Treatment may involve medications such as blood thinners or clot-busting drugs, or in some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the clot.
Prevention of blood clots in the brain involves lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, regular exercise, and managing underlying medical conditions. If you have a family history of blood clots or have other risk factors, talk to your doctor about steps you can take to reduce your risk.
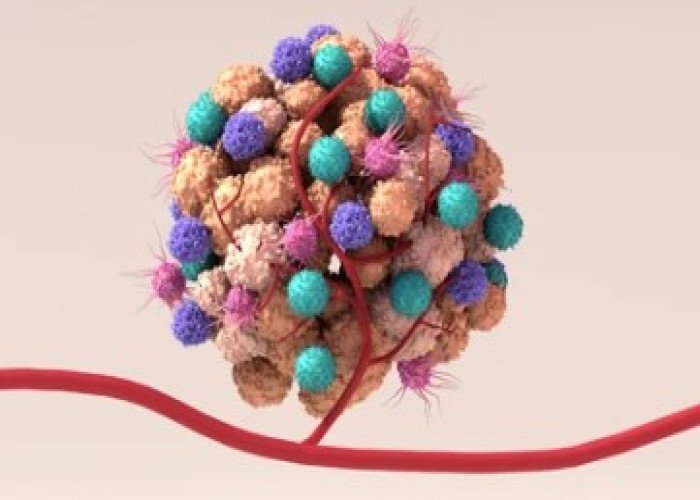
Tumor

Syphilis
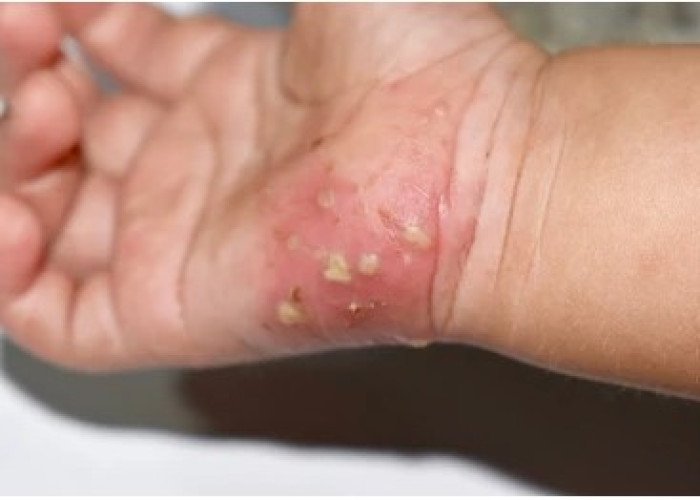
Scabies
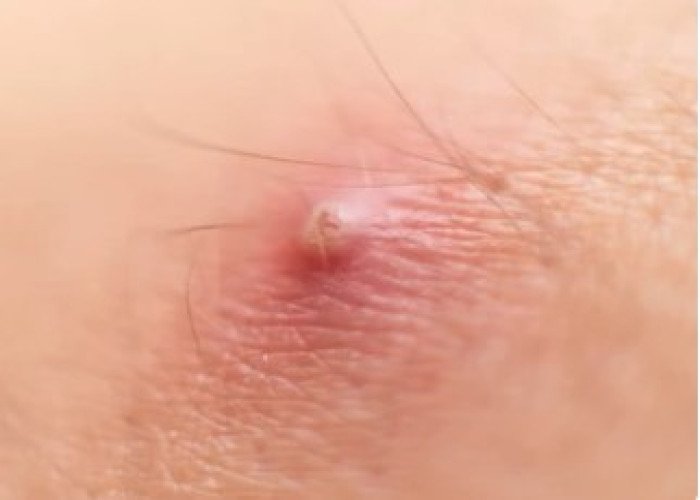
Malignant boil
Growth retardation

Nervous headache

Acne

Tonsillitis
Blood clots in brain, মস্তিষ্কে রক্ত জমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.