 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
Acute trauma - Generics
Acute trauma refers to a sudden injury or shock to the body that can be caused by various factors such as accidents, falls, physical violence, or natural disasters.
Symptoms of acute trauma can vary depending on the type and severity of the injury, but can include pain, swelling, bruising, bleeding, fractures, dislocations, and traumatic brain injury. In some cases, acute trauma can also lead to shock, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Treatment for acute trauma depends on the type and severity of the injury. It may involve first aid measures such as stopping bleeding, immobilizing injured limbs, or providing oxygen, as well as more advanced medical interventions such as surgery or medications.
Prevention of acute trauma involves taking steps to minimize the risk of injury, such as wearing protective gear during sports or high-risk activities, following safety protocols in the workplace, and avoiding high-risk behaviors such as driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
If you or someone you know has experienced acute trauma, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Early intervention and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.

Balanced anesthesia
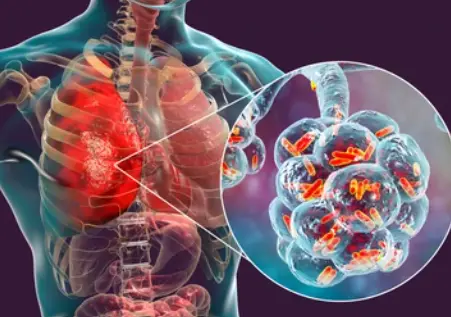
Bacteraemic pneumonia

Disinfection
Chemotherapy-induced naus...

Cardiovascular disease

Aspergillosis

Age-related macular degen...

Angular cheilitis
Acute trauma, তীব্র ট্রমা
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.