 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Novoxen 375mg + 20mg
Xenole 500mg + 20mg
Progesic 375mg + 20mg
Naprotec 375mg + 20mg
Progut-N 500mg + 20mg
Naspro Plus 375mg + 20mg
Novaxen Plus 500mg + 20mg
Solivo 375mg + 20mg
Xenapro Plus 500mg + 20mg
Duofix 500mg + 20mg
Solivo 500mg + 20mg
Naprosyn Plus 375mg + 20mg
Naproxzia Plus 500mg + 20mg
Napsec 500mg + 20mg
Napsec 375mg + 20mg
NX Plus 375mg + 20mg
Tablet (Delayed Release) - Brands
A delayed-release tablet is a type of medication that is designed to release the active ingredient at a specific time or location in the digestive system. These tablets are formulated with a special coating or matrix that prevents the drug from being released in the stomach, where it may be destroyed by stomach acid, and instead delivers the drug to the intestines.
Delayed-release tablets are commonly used to treat conditions that require medication to be absorbed in the intestines, such as inflammatory bowel disease or acid reflux. By delivering the drug to the intestines, delayed-release tablets can help to ensure that the drug is absorbed properly and that the patient receives the full therapeutic benefit.
The timing and location of drug release from a delayed-release tablet can be influenced by a number of factors, including the properties of the drug, the type of coating or matrix used, and the pH and composition of the digestive fluids in the body. As a result, it is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper use of delayed-release tablets, including any instructions regarding how to take the medication and any potential interactions with other medications.
It is important to note that delayed-release tablets should not be crushed or chewed, as this can affect the timing and location of drug release and potentially lead to an overdose or other adverse effects. As with any medication, patients should follow their healthcare provider's instructions for proper use and be aware of any potential side effects or interactions with other medications.
How to use Tablet (Delayed Release)?
Delayed-release tablets are designed to release the medication at a specific time or location in the digestive tract. Here are the general steps for using a delayed-release tablet:
- Read the medication label carefully to make sure you understand how to take the medication.
- Swallow the tablet whole with water. Do not crush, chew, or break the tablet, as this can affect the way the medication is released.
- Take the tablet at the same time each day or as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Some delayed-release tablets should be taken with food, while others should be taken on an empty stomach. Be sure to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider or the medication packaging.
- Do not drink alcohol while taking the medication, as this can increase the risk of side effects.
- Do not change the dose or stop taking the medication without consulting with your healthcare provider.
It is important to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider or the medication packaging. If you have any questions or concerns about how to use a delayed-release tablet, be sure to consult with your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
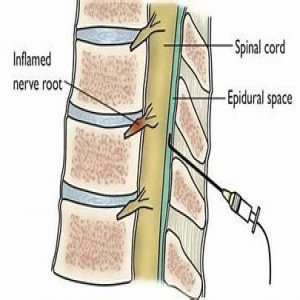
Injection

Cream

Mouthwash
Gel

MUPS Tablet

Syrup

Oral Gel

Suspension
Delayed Release Tablet, How to use Delayed Release Tablet, বিলম্বিত রিলিজ ট্যাবলেট, DR Tablet, ডিআর ট্যাবলেট
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.