 Welcome
Welcome
“May all be happy, may all be healed, may all be at peace and may no one ever suffer."
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- F
- G
- H
- I
- J
- K
- L
- M
- N
- O
- P
- Q
- R
- S
- T
- U
- V
- W
- X
- Y
- Z
Trialon 0.10%
Trimcort 0.10%
Oral Paste - Brands
An oral paste is a type of medication that is administered orally and has a thick, sticky consistency. It is a semisolid formulation that is typically applied directly to the tongue or inside of the cheek, where it can be absorbed through the mucous membranes.
Oral pastes are used to treat a variety of conditions, including fungal infections, fever blisters, and canker sores. They may contain different types of active ingredients, such as antifungal agents, antiviral drugs, or anti-inflammatory medications.
Oral pastes are designed to provide targeted and localized relief to the affected area. They are typically applied using a syringe or applicator and can be left in place for a short period of time to allow the medication to be absorbed.
Oral pastes are generally safe and effective when used as directed, but they may cause some temporary numbness or other mild discomfort in the mouth. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare provider and to inform them of any side effects or allergic reactions. In addition, some oral pastes may contain sugar or other ingredients that can be harmful to individuals with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using an oral paste if you have any medical conditions or are taking any medications.
How to use Oral Paste?
Here are some general guidelines on how to use an oral paste:
- Wash your hands: Before using the oral paste, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Measure the dose: Using a calibrated measuring device or a clean spoon, measure the prescribed amount of oral paste. Make sure you follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider or the manufacturer of the oral paste.
- Apply the paste: Apply the oral paste directly to the affected area of the mouth or gums using your finger or a cotton swab. If you are using a cotton swab, discard it after use to prevent contamination.
- Allow the paste to stay in place: After applying the oral paste, avoid eating or drinking for at least 30 minutes to allow the paste to stay in place and work effectively.
- Replace the cap: Replace the cap tightly on the oral paste tube or bottle and store it in a cool, dry place.
It's important to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and the manufacturer of the oral paste. If you have any questions or concerns about how to use an oral paste, speak with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Be sure to follow the recommended dosing and frequency for the paste to ensure safe and effective use. Additionally, if you are using other medications or supplements, check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist to determine if there are any potential interactions with the oral paste.

Effervescent Granules
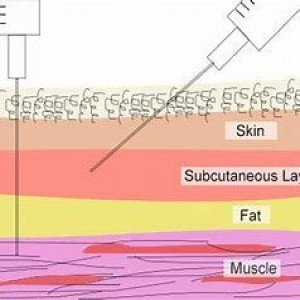
Injection

Liquid

Syrup

Capsule (TR)
LA Injection

Emulsion

Oral Solution
Oral Paste, How to use Oral Paste, ওরাল পেস্ট
To be happy, beautiful, healthy, wealthy, hale and long-lived stay with DM3S.